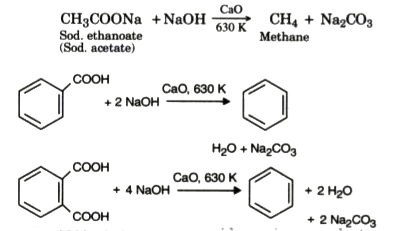
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-SOME IMPORTANT ORGANIC NAME REACTIONS -Questions
- Cope rearrangement
Text Solution
|
- Darzen's process.
Text Solution
|
- Decarboxylation.
Text Solution
|
- Diazotisation
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds would undergo Diels-Alder reaction wi...
Text Solution
|
- Dow process.
Text Solution
|
- Elb's reaction
Text Solution
|
- Esterification Reaction or Fisher esterification.
Text Solution
|
- Etard's Reaction.
Text Solution
|
- E(2) reaction (Elimination bimolecular reaction)
Text Solution
|
- E(1) reaction (Elimination unimolecular reaction).
Text Solution
|
- Exhaustive alkylation.
Text Solution
|
- Finkelstein reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Fischer-Tropsch process.
Text Solution
|
- Frankland's reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Fries Rearrangement
Text Solution
|
- Friedel - Crafts alkylation
Text Solution
|
- Friedel - Crafts acylation
Text Solution
|
- Fittig's reaction
Text Solution
|
- Favorskii rearrangement
Text Solution
|