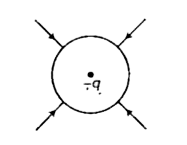
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Electric Flux through Spherical Gaussian Surface A point charge caus...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an electric flux of -1.0xx10^(3) N m^(2)//C to p...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an electric flux of -1.0xx10^(3) Nm^(2)//C to pa...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an elelctric flux of -1.0 xx10^(3) Nm^(2) /C to...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an electric flux of -1.0xx10^(3) N m^(2)//C to p...
Text Solution
|
- A point charges causes an electric flux of -1.0 xx10^(3) Nm^(2) //C to...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an electric flux of-1.0 xx 10^3 Nm^2//C to pass ...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an electric flux of -1.0xx10^(3) N m^(2)//C to p...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an electric flux of -1.0xx10^3Nm^2//C to pass th...
Text Solution
|