A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
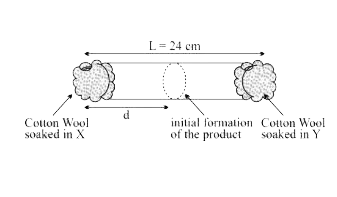
- X and Y are two volatile liquids with molar weights of 10g mol^(-1) an...
Text Solution
|
- X and Y are two volatile liquids with molar weights of 10gmol^(-1) and...
Text Solution
|
- X and Y are two volatile liquids with molar weights of 10gmol^(-1) and...
Text Solution
|
- Vapour pressure of a pure liquid X is 2 atm at 300 K. It is lowered to...
Text Solution
|
- Two liquids X and Y form an ideal solution. At 300 K, vapour pressure ...
Text Solution
|
- X और Y, क्रमशः 10g ”मोल”^(-1) एवं 40g ”मोल”^(-1) के वाष्पशील द्रव हैं।...
Text Solution
|
- X और Y, क्रमशः 10g ”मोल”^(-1) एवं 40g ”मोल”^(-1) के वाष्पशील द्रव हैं।...
Text Solution
|
- X और Y, क्रमशः 10g mol^(-1) एवं 40g mol^(-1) के वाष्पशील द्रव हैं। दो ...
Text Solution
|
- X और Y, क्रमशः 10g ”मोल”^(-1) एवं 40g ”मोल”^(-1) के वाष्पशील द्रव हैं।...
Text Solution
|