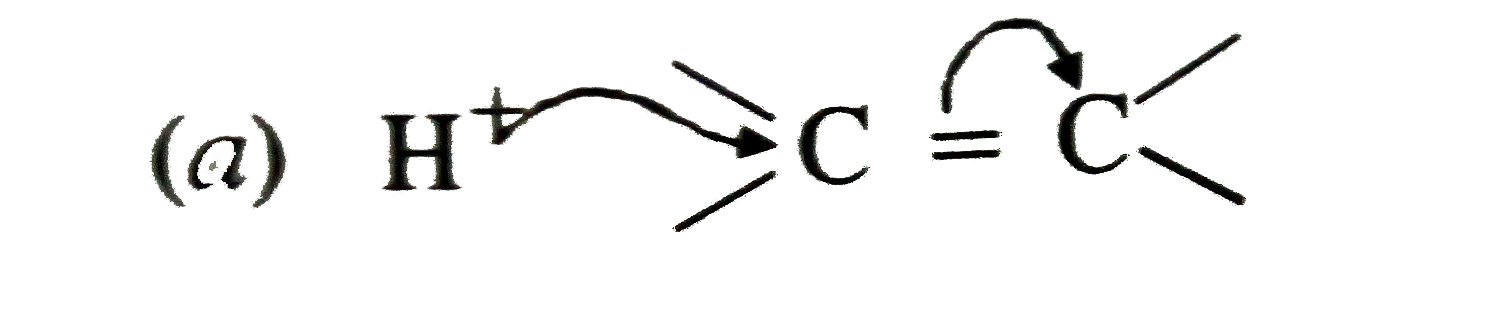A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The additions of HCl to an alkene proceeds in two steps. The first ste...
Text Solution
|
- Electrophillic addition reaction proceed in two steps. The first step ...
Text Solution
|
- The addition of HCl to an alkene proceeds in two steps. The first step...
Text Solution
|
- Electrophilic additions reactions proceed in two steps. The first step...
Text Solution
|
- The additions of HCl to an alkene proceeds in two steps. The first ste...
Text Solution
|
- Electrophilic additions reactions proceed in two steps. The first step...
Text Solution
|
- The addition of HCl to an alkene proceeds in two steps. The first step...
Text Solution
|
- Electrophilic addition reactions proceed in two steps. The first step ...
Text Solution
|
- The first step in the attack of nucleophile on the alkene is?
Text Solution
|
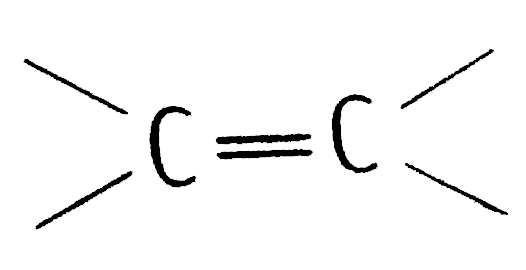 portion which can be shown as
portion which can be shown as