The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two `pi`-bonds or between a `pi`-bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacentatom.' The effect is transmitted through the chain.
In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system.
Which of the following shows +M effect ?
The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two `pi`-bonds or between a `pi`-bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacentatom.' The effect is transmitted through the chain.
In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system.
Which of the following shows +M effect ?
In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system.
Which of the following shows +M effect ?
A
`- N(CH_(3))_(2)`
B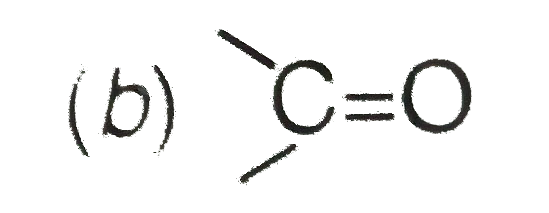
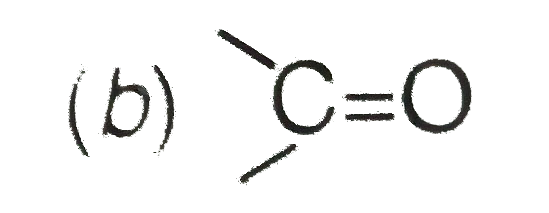
C
`- CN`
D
Both (a) and (c)
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
To determine which of the following groups shows a positive resonance effect (+M effect), we need to analyze the given groups based on their ability to donate electron density through resonance. Here’s a step-by-step solution:
### Step 1: Understand the Positive Resonance Effect
The positive resonance effect (+M effect) occurs when a substituent group donates electron density to a conjugated system. This typically involves groups that have lone pairs of electrons that can participate in resonance with the π-system of the molecule.
**Hint:** Look for groups with lone pairs that can interact with adjacent π-bonds.
### Step 2: Analyze the Given Groups
1. **Ammonia (NH3)**:
- Ammonia has a lone pair on nitrogen. When attached to a conjugated system (like benzene), the lone pair can resonate into the π-system, donating electron density. Thus, it shows a +M effect.
2. **Carbonyl Group (C=O)**:
- The carbonyl group is an electron-withdrawing group because the oxygen is more electronegative than carbon. It pulls electron density away from the conjugated system, showing a -M effect.
3. **Cyanide Group (CN)**:
- The cyanide group also has a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. The nitrogen is more electronegative and pulls electron density towards itself, indicating a -M effect.
### Step 3: Conclusion
From the analysis:
- **Ammonia (NH3)** shows a +M effect.
- **Carbonyl Group (C=O)** and **Cyanide Group (CN)** both show a -M effect.
Thus, the group that shows a +M effect is **Ammonia (NH3)**.
### Final Answer
**Ammonia (NH3) shows the +M effect.**
---
To determine which of the following groups shows a positive resonance effect (+M effect), we need to analyze the given groups based on their ability to donate electron density through resonance. Here’s a step-by-step solution:
### Step 1: Understand the Positive Resonance Effect
The positive resonance effect (+M effect) occurs when a substituent group donates electron density to a conjugated system. This typically involves groups that have lone pairs of electrons that can participate in resonance with the π-system of the molecule.
**Hint:** Look for groups with lone pairs that can interact with adjacent π-bonds.
### Step 2: Analyze the Given Groups
...
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi -bonds or between a pi -bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacentatom.' The effect is transmitted through the chain. In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. Which of the following does not show resonance effect ?
The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi -bonds or between a pi -bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacentatom.' The effect is transmitted through the chain. In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. Which of the following carboxylate ions is the most stable ?
The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi -bonds or between a pi -bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacentatom.' The effect is transmitted through the chain. In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. What is the IUPAC name for :
The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi -bonds or between a pi -bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacentatom.' The effect is transmitted through the chain. In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. Which of the following intermediates is pyramidal in shape ?
The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi -bonds or between a pi -bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom.' The effect is transmitted through the chain. In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. Which of the following free radicals is the most stable ?
The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi -bonds or between a pi -bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacentatom.' The effect is transmitted through the chain. In positive resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is away from an atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. This electron displacement makes certain positions in the molecule of high electron densities. In negative resonance effect, the transfer of electrons is towards the atom or substituent group attached to the conjugated system. The correct statement regarding a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha carbon, is
In this molecules, pi -electron density is more on :
In this molecules, pi- electron - density is more on
Due to screening effect of electrons in an atom
The number of lone pair of electrons on each atom of oxygen molecule is
Recommended Questions
- The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molec...
Text Solution
|
- The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molec...
Text Solution
|
- The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molec...
Text Solution
|
- The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molec...
Text Solution
|
- The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molec...
Text Solution
|
- The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molec...
Text Solution
|
- The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molec...
Text Solution
|
- The resonance effect is defined as 'the polarity produced in the molec...
Text Solution
|
- Mesomeric or resonance effect is a permanent effect involving the tran...
Text Solution
|