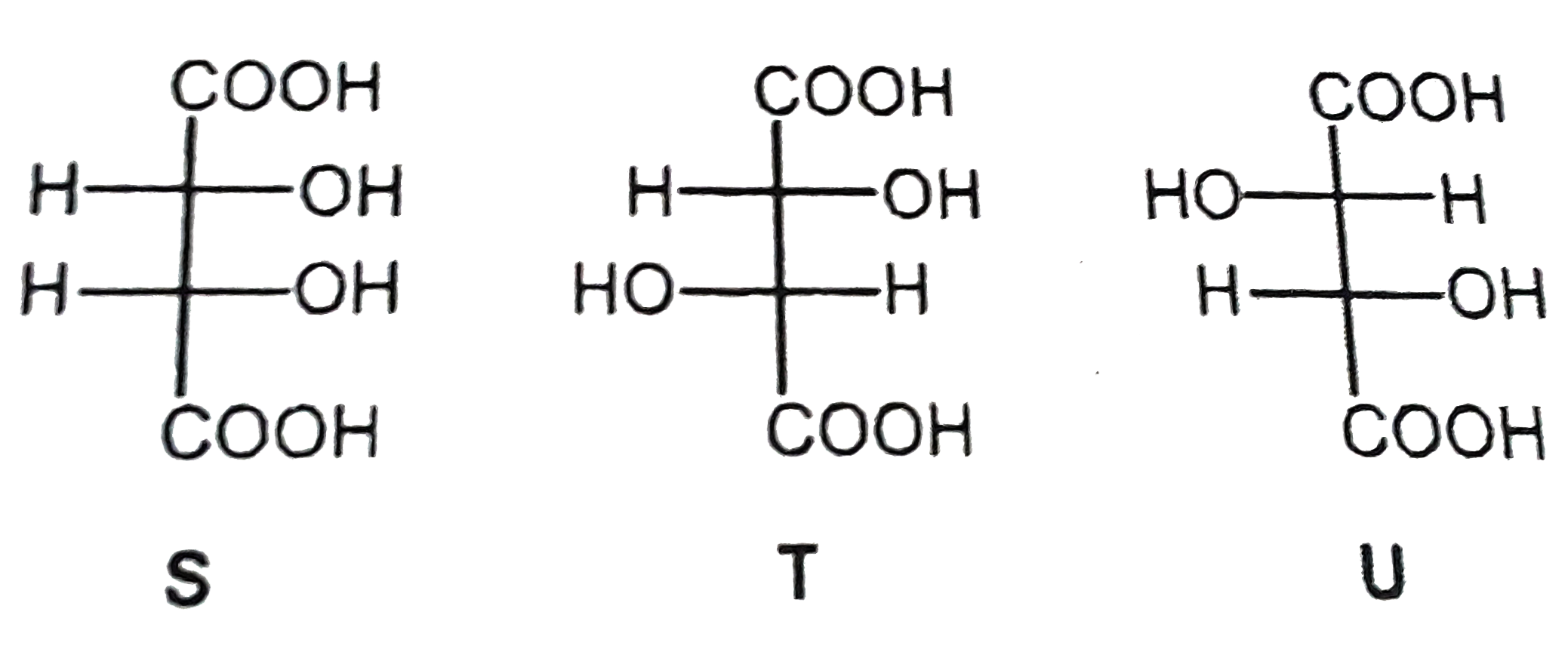
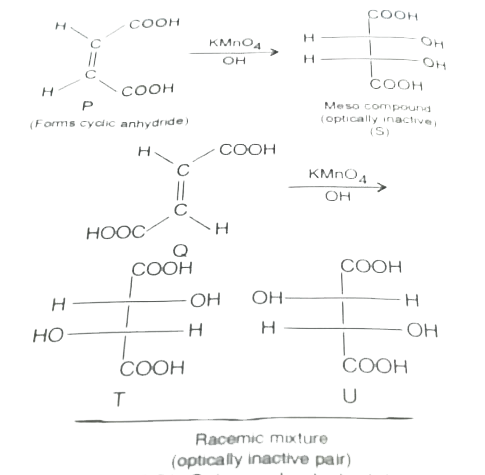
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acid C(4)H(4)O(4). Both decolorize...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acid C(4)H(4)O(4) . Bothdecolorize...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomer of dicraboxylic acid C(4)H(4)O(4) Both decolourixe ...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomer of dicraboxylic acid C(4)H(4)O(4) Both decolourixe ...
Text Solution
|
- Q. C(3)H(2)O(2)underset(KMnO(4))overset("Hot alkaline")toProduct. One ...
Text Solution
|
- Compound 'P'(C(10)H(12)O) evolves H(2) gas with Na metal. It reaches w...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomers of dicarboxyhc acid C(4)H4O(4) .Both decolourize B...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acid C(4)H(4)O(4). Both decolorize...
Text Solution
|
- P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acid C(4)H(4)O(4). Both decolorize...
Text Solution
|