A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
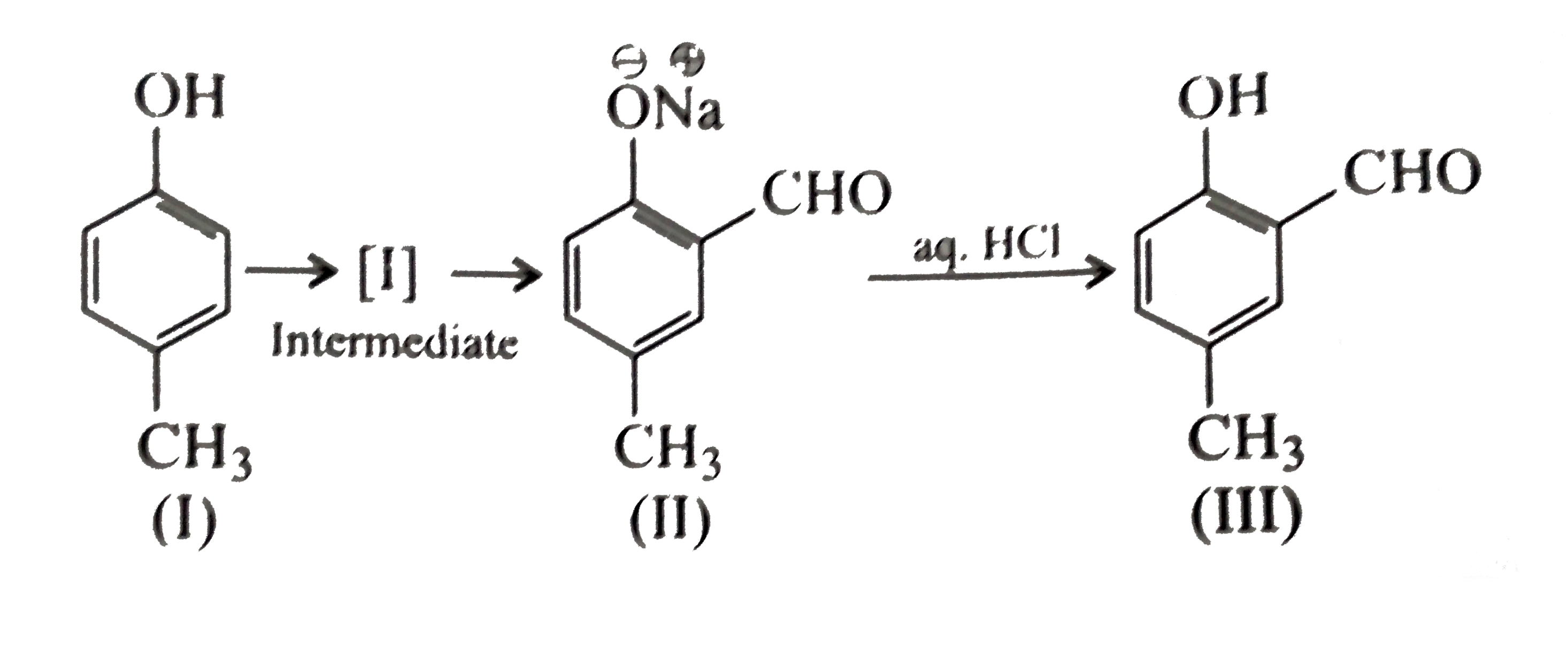
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group on to the aromati...
Text Solution
|
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group on to the aromati...
Text Solution
|
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group on to the aromati...
Text Solution
|
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group on to the aromati...
Text Solution
|
- Reimer Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group, on to the ring o...
Text Solution
|
- Reimer Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group, on to the ring o...
Text Solution
|
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group on to the aromati...
Text Solution
|
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group on to the aromati...
Text Solution
|
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction introduces an aldehyde group on to the aromati...
Text Solution
|