Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS-All Questions
- Find sum(k=1)^6 (sin,(2pik)/7 -icos, (2pik)/7)=?
Text Solution
|
- If the equation a x^2+b x+c=0(a >0) has two real roots alphaa n db...
Text Solution
|
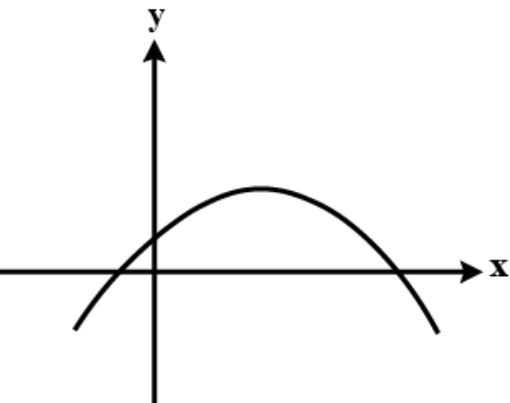
- If fig shows the graph of f(x)=a x^2+b x+c ,t h e n Fig a. c<...
Text Solution
|
- If |[6i,-3i,1],[ 4, 3i,-1],[ 20, 3,i]|=x+i y , then a.x=3,y=1 b. x=1,y...
Text Solution
|
- Let z=x+i y be a complex number, where xa n dy are real numbers. Let...
Text Solution
|
- If z=((sqrt(3))/2+i/2)^5+((sqrt(3))/2-i/2)^5 , then prove that I m(z)=...
Text Solution
|
- The value of sum(n=1)^(13) (i^n+i^(n+1)), where i =sqrt(-1) equals ...
Text Solution
|
- If c!=0 and the equation p//(2x)=a//(x+c)+b//(x-c) has two equal roots...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation 4x^2-x-1=0 and 3x^2+(lambda+mu)x+lambda-mu=0 have a r...
Text Solution
|
- Express the following in a+i b form: ((cos2theta-isin2theta)^4(cos4...
Text Solution
|
- The roots of the equation t^3+3a t^2+3b t+c=0a r ez1, z2, z3 which rep...
Text Solution
|
- Solve the equation (x-1)^3+8=0 in the set C of all complex numbers.
Text Solution
|
- If 'z, lies on the circle |z-2i|=2sqrt2, then the value of arg((z...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation whose roots are the squares of the roots of the cubic ...
Text Solution
|
- If sqrt(3)+i=(a+i b)(c+i d) , then find the value of tan^(-1)(b//a)+ta...
Text Solution
|
- P(z) be a variable point in the Argand plane such that |z|=minimum {|z...
Text Solution
|
- If the equation a x^2+b x+c=0,a ,b ,c , in R have none-real roots, t...
Text Solution
|
- Prove that the equation Z^3+i Z-1=0 has no real roots.
Text Solution
|
- The locus of point z satisfying Re(1/z)=k, where k is a non-zero real ...
Text Solution
|
- If p(q-r)x^2+q(r-p)x+r(p-q)=0 has equal roots, then prove that 2/q=1/p...
Text Solution
|