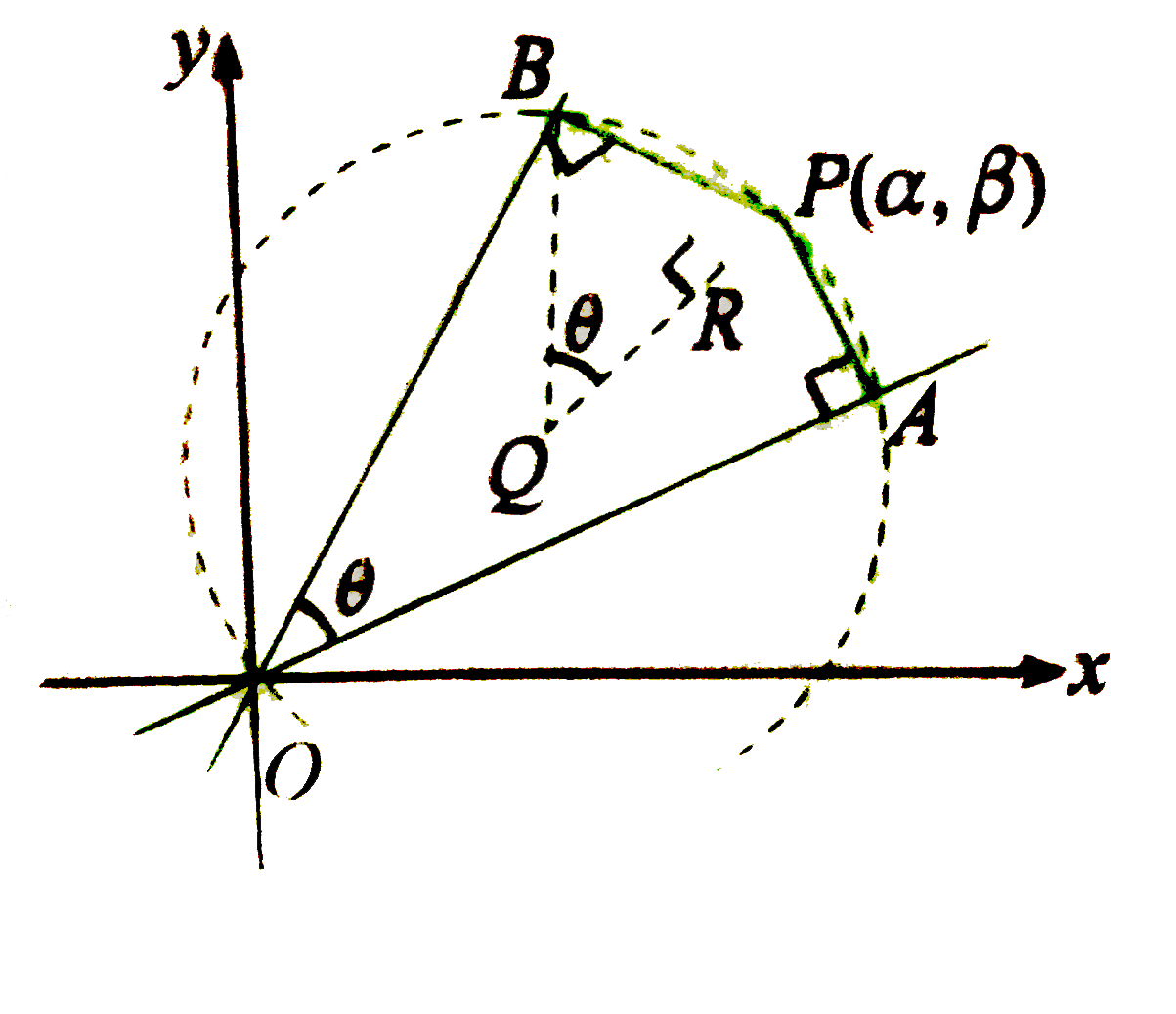Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PAIR OF STRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Exercise 3.1|6 VideosPAIR OF STRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Exercise 3.2|7 VideosPAIR OF STRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Illustration 3.17|1 VideosMONOTONOCITY AND NAXINA-MINIMA OF FUNCTIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Comprehension Type|6 VideosPARABOLA
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Matching Column Type|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-PAIR OF STRAIGHT LINES-Solved Examples
- Show that straight lines (A^2-3B^2)x^2+8A Bx y+(B^2-3A^2)y^2=0 form wi...
Text Solution
|
- Product of the perpendiculars from (alpha, beta) to the lines ax^2+2hx...
Text Solution
|
- The distance of a point (x1, y1) from two straight lines which pass th...
Text Solution
|
- A point moves so that the distance between the foot of perpendiculars ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that all chords of the curve 3x^2-y^2-2x+4y=0, which subtend a ri...
Text Solution
|