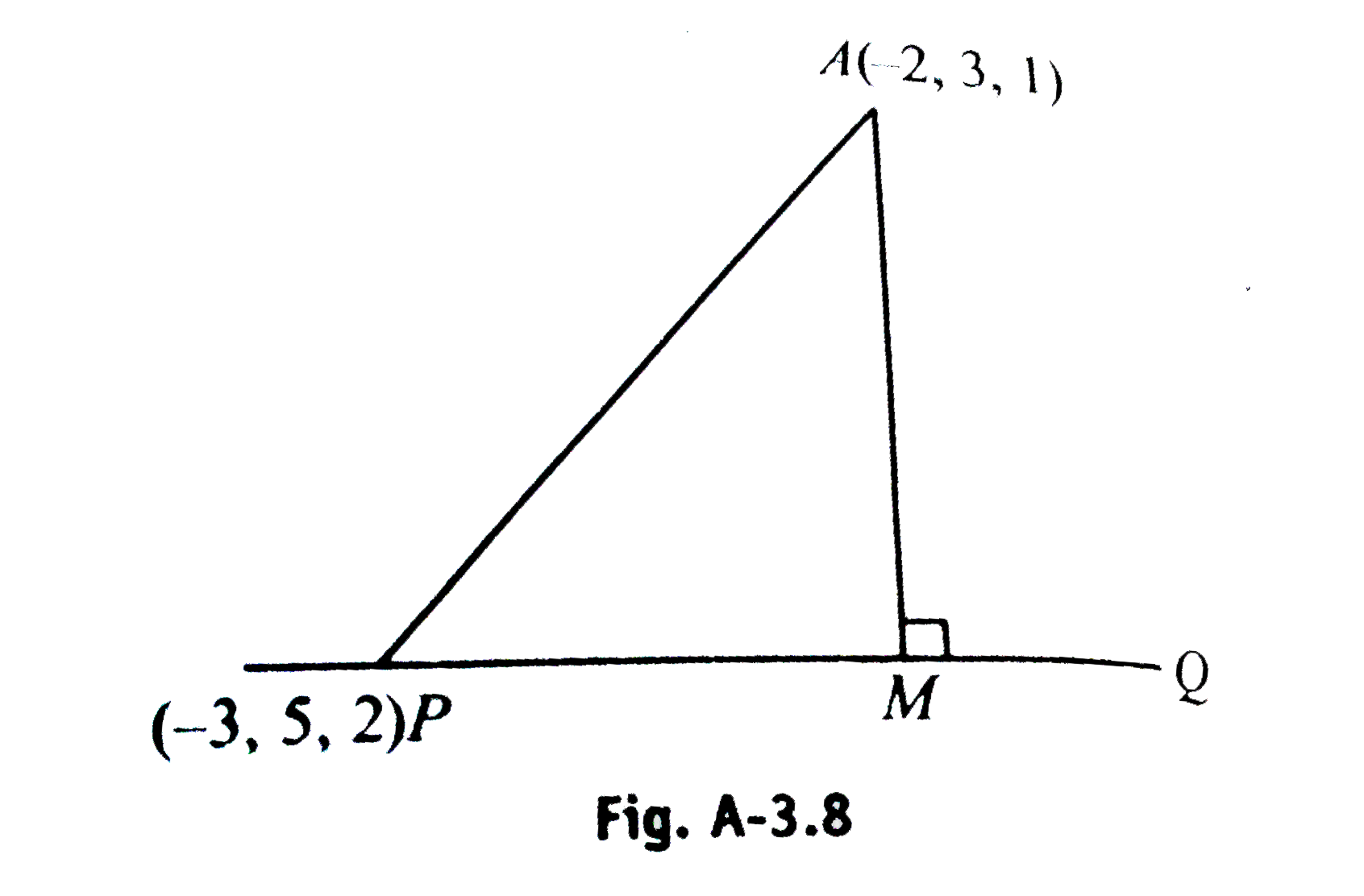A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise MULTIPLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE|17 VideosTHREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise REASONING TYPE|10 VideosTHREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise SUBJECTIVE TYPE|17 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise All Questions|291 VideosTRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Archives (Numerical value type)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY -SINGLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE
- Let the equations of a line and plane be (x+3)/2=(y-4)/3=(z+5)/2a n...
Text Solution
|
- The length of the perpendicular from the origin to the plane passing t...
Text Solution
|
- The distance of point A(-2,3,1) from the line P Q through P(-3,5,2), w...
Text Solution
|
- The Cartesian equation of the plane vec r=(1+lambda-mu) hat i+(2-l...
Text Solution
|
- A unit vector parallel to the intersection of the planes vec r. \ (...
Text Solution
|
- Let L1 be the line vec r1=2 hat i+ hat j- hat k+lambda(hat i+2 hat k)...
Text Solution
|
- For the line (x-1)/1=(y-2)/2=(z-3)/3, which one of the following is...
Text Solution
|
- The value of m for which the straight line 3x-2y+z+3 = 0=4x-3y+4z+1. i...
Text Solution
|
- The intercept made by the plane vec r . vec n=q on the x-axis is a. q...
Text Solution
|
- Equation of a line in the plane pi-=2x-y+z-4=0 which is perpendicul...
Text Solution
|
- If the foot of the perpendicular from the origin to plane is P(a ,b...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of the plane which passes through the point of interse...
Text Solution
|
- Let A( vec a)a n dB( vec b) be points on two skew lines vec r= vec a+...
Text Solution
|
- Let A(1,1,1),B(2,3,5)a n dC(-1,0,2) be three points, then equation of ...
Text Solution
|
- The point on the line (x-2)/1=(y+3)/(-2)=(z+5)/(-2) at a distance of 6...
Text Solution
|
- The coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the orig...
Text Solution
|
- If P1:vec r.vecn1-d1=0 P2:vec r.vec n2-d2=0 and P3:vec r.vecn3-d3=0 ar...
Text Solution
|
- The length of projection of the line segment joining the points (1,0,-...
Text Solution
|
- The number of planes that are equidistant from four non-coplanar po...
Text Solution
|
- In a three-dimensional coordinate system, P ,Q ,a n dR are images o...
Text Solution
|