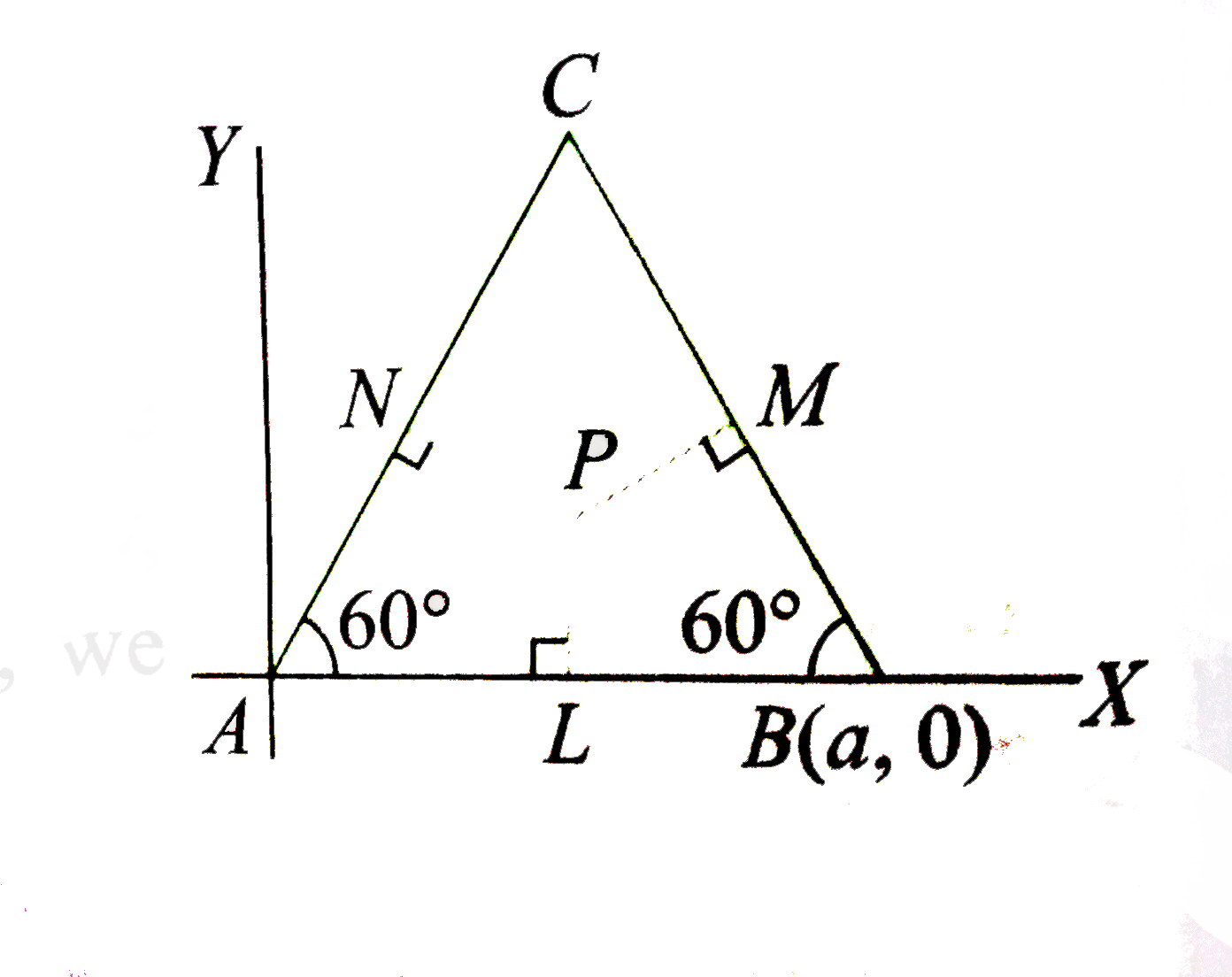Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
STRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise EXAMPLE|12 VideosSTRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 2.1|23 VideosSTRAIGHT LINE
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|8 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise JEE ADVANCED (Numerical Value Type )|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems