Given lines are
`L_(1) (x,y) = 2x+3y-1 = 0`
`L_(2) (x,y) = 5x-6y-1 = 0`
`L_(3) (x,y) = x+2y-3 = 0`
Draw these lines on coordinate axes.
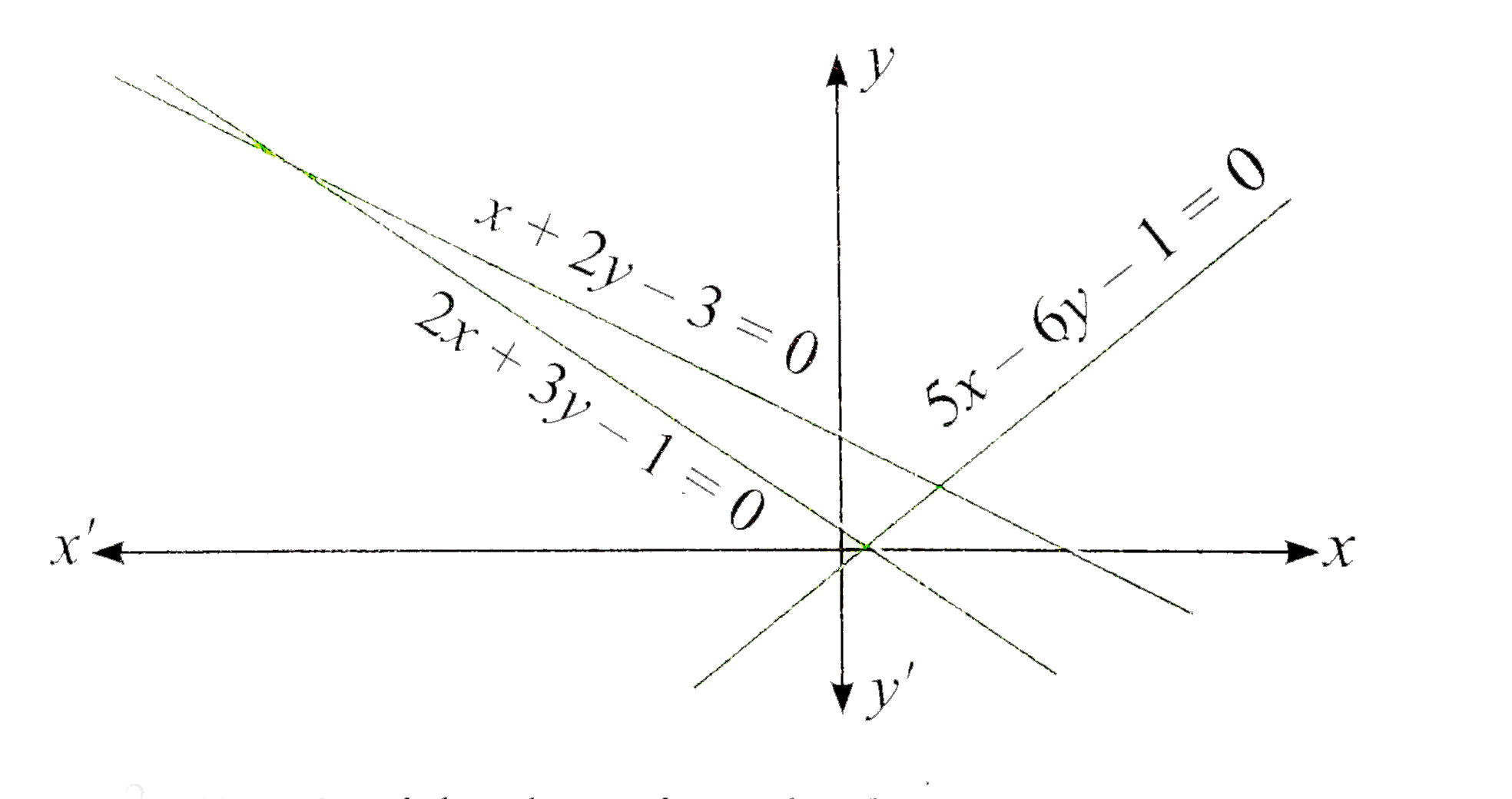
Point `P(alpha, alpha^(2))` lies inside the triangle formed by these lines.
Clearly, from the figure, origin and point P lie on the opposite side w.r.t 2x+3y-1=0.
`L_(1)(0,0) = -1 lt 0`
So, we must have
`L_(1) (alpha, alpha^(2)) =2alpha + 3alpha^(2)-1 gt 0`
`rArr (3alpha - 1)(alpha+ 1) gt 0`
`rArr alpha lt - 1 or alpha gt 1//3 " " (1)`
Also, origin and point P lie on the same side w.r.t line
x+2y-3=0.
`L_(3)(0,0) = -3 lt 0`
So, we must have `L_(3)(alpha,alpha^(2)) = alpha + 2alpha^(2) -3 lt 0`
`rArr (2alpha + 3)(alpha -1) lt 0`
`rArr -3//2 lt alpha lt 1 " " (2)`
Further origin and point P lie on the same side w.r.t. line
5x-6y-1=0.
`rArr L_(2)(0,0) = -1 lt 0`
So, we must have
` L_(2)(alpha, alpha^(2)) = 5alpha-6alpha^(2)-1 lt 0`
`rArr 6alpha^(2)-5alpha + 1 gt 0`
`rArr (3alpha-1)(2alpha-1) gt 0`
`rArr alpha lt 1//3 or alpha gt 1//2 " " (3)`
From (1), (2) and (3), common values of `alpha` are (-3/2,-1)`uu` (1/2,1).
