Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
STRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 2.1|23 VideosSTRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 2.2|4 VideosSTRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise ARCHIVES (NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE)|1 VideosSTRAIGHT LINE
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|8 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise JEE ADVANCED (Numerical Value Type )|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-STRAIGHT LINES-EXAMPLE
- Show that the lines 4x+y-9=0,x-2y+3=0,5x-y-6=0 make equal intercepts o...
Text Solution
|
- The equations of two sides of a triangle are 3y-x-2=0a n dy+x-2=0. The...
Text Solution
|
- Find the locus of the circumcenter of a triangle whose two sides are ...
Text Solution
|
- Let A B C be a triangle with A B=A Cdot If D is the midpoint of B C ,E...
Text Solution
|
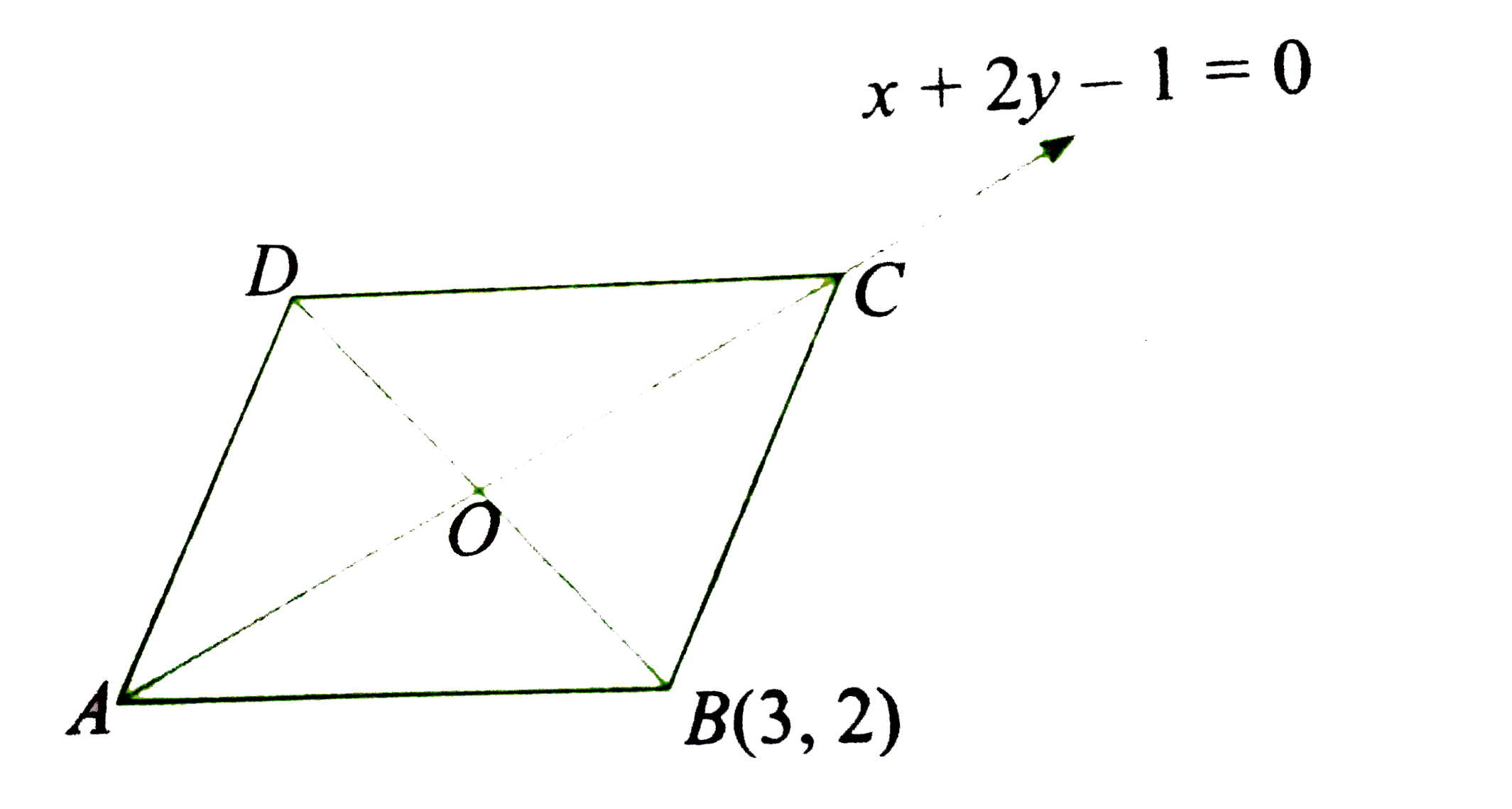
- A diagonal of rhombus A B C D is member of both the families of lines ...
Text Solution
|
- Let A B C be a given isosceles triangle with A B=A C . Sides A Ba n dA...
Text Solution
|
- Let L1=0a n dL2=0 be two fixed lines. A variable line is drawn through...
Text Solution
|
- Let points A,B and C lie on lines y-x=0, 2x-y=0 and y-3x=0, respective...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two lines L1a n dL2 given by x-y=0 and x+y=0 , respectively, ...
Text Solution
|
- Let O(0,0),A(2,0),a n dB(1, 1/(sqrt(3))) be the vertices of a triangle...
Text Solution
|
- A line through A(-5,-4) meets the lines x+3y+2=0, 2x+y+4=0 and x-y-5=0...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangle PQRS has its side PQ parallel to the line y= mx and verti...
Text Solution
|