Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
AREA
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Concept Application Exercise 9.1|9 VideosAREA
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Concept Application Exercise 9.2|14 VideosAREA
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Comprehension Type|2 VideosAPPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Subjective Type|2 VideosBINOMIAL THEOREM
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Comprehension|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-AREA-Solved Examples
- Find the area bounded by the curve x^2=y ,x^2=-y and y^2=4x-3
Text Solution
|
- Find the area of the region enclosed by the curve y=|x-(1)/(x)|(xgt0) ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the area of the region bounded by the curves y=x^2,y=|2-x^2|,a n ...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio in which the line x-1=0 divides the area bounded by the curv...
Text Solution
|
- If S(0),S(1),S(2),… are areas bounded by the x-axis and half-wave of t...
Text Solution
|
- Find the area of the figure enclosed by the curve 5x^2+6x y+2y^2+7x+6y...
Text Solution
|
- Find the area bounded by the curves x^2+y^2=4,x^2=sqrt(2)y ,a n dx=ydo...
Text Solution
|
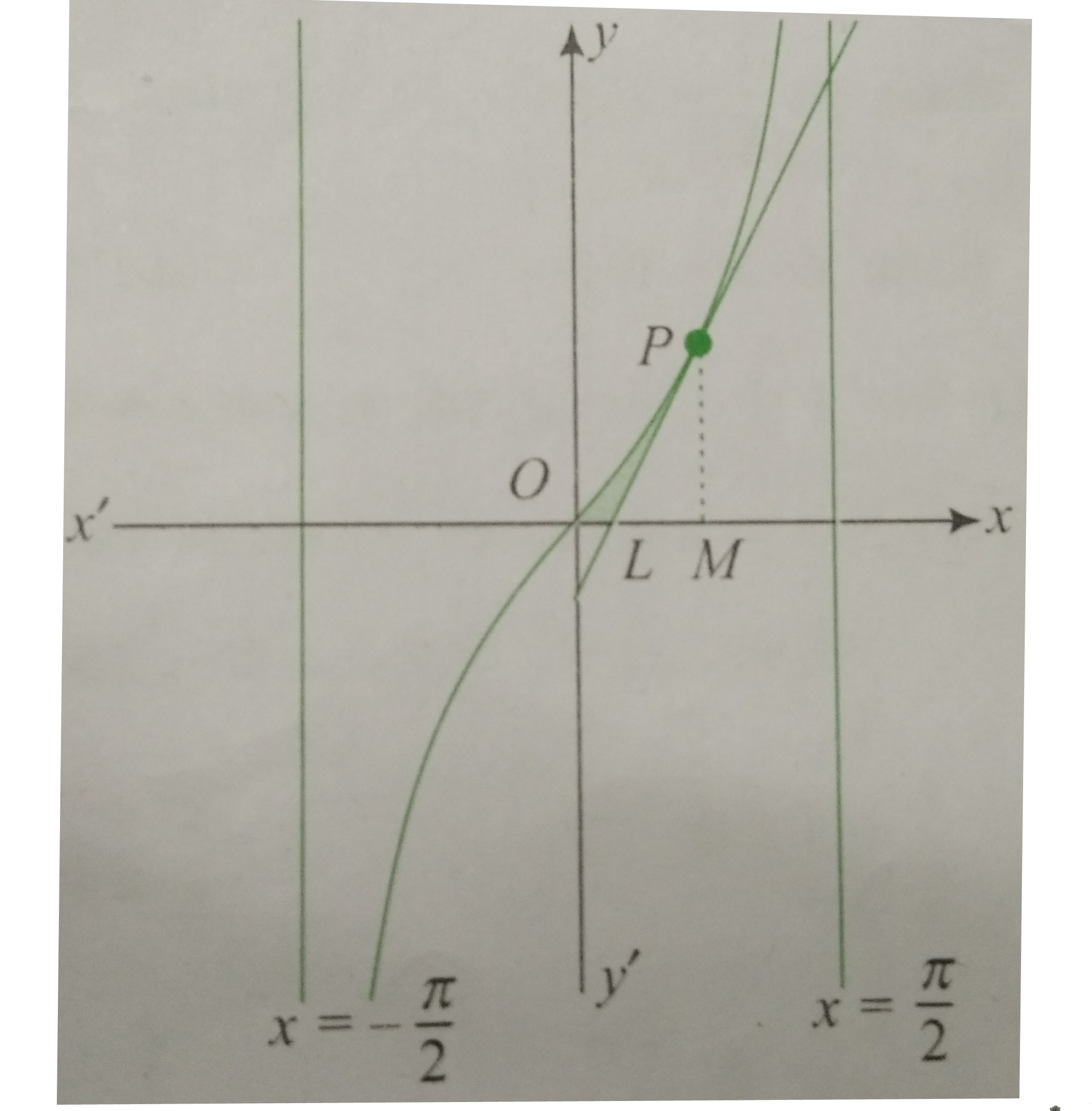
- Find the area of the region bounded by the curve C : y=tan x ,tangent ...
Text Solution
|
- Compute the area of the region bounded by the curves y-e x(log)e xa n ...
Text Solution
|
- If An be the area bounded by the curve y=(tanx)^n and the lines x=0,\ ...
Text Solution
|