A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
AREA
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Matrix Match Type|5 VideosAREA
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Numerical Value Type|18 VideosAREA
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|13 VideosAPPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Subjective Type|2 VideosBINOMIAL THEOREM
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Comprehension|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-AREA-Linkded Comprehension Type
- Let A(r) be the area of the region bounded between the curves y^(2)=(e...
Text Solution
|
- If y=f(x) is a monotonic function in (a,b), then the area bounded by t...
Text Solution
|
- If y=f(x) is a monotonic function in (a,b), then the area bounded by t...
Text Solution
|
- If y=f(x) is a monotonic function in (a,b), then the area bounded by t...
Text Solution
|
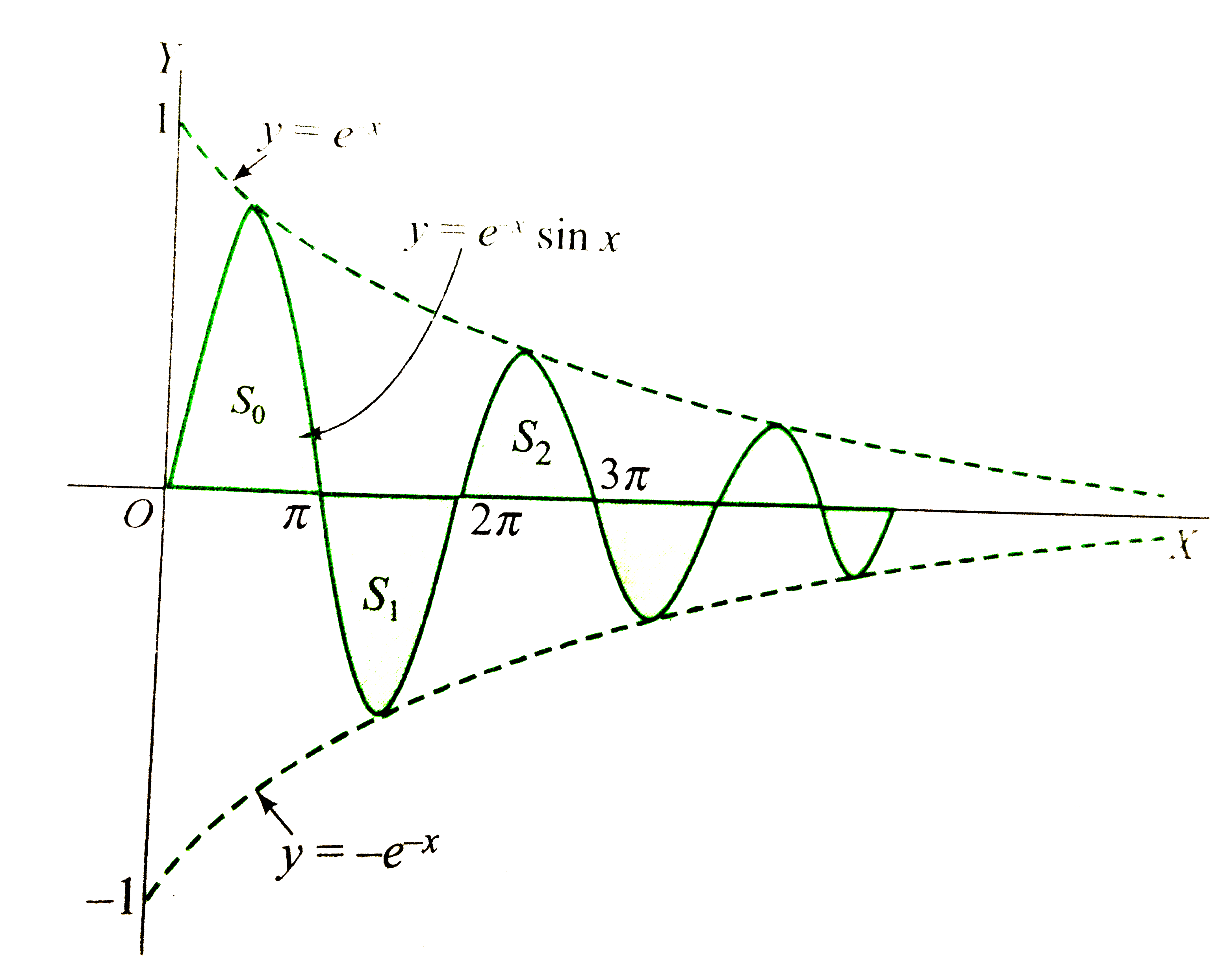
- If S(0),S(1),S(2),… are areas bounded by the x-axis and half-wave of t...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the sequence of natural numbers S0,S1,S2,... such that S0 =3,...
Text Solution
|
- If S(0),S(1),S(2),… are areas bounded by the x-axis and half-wave of t...
Text Solution
|
- Two curves C(1)equiv[f(y)]^(2//3)+[f(x)]^(1//3)=0 and C(2)equiv[f(y)]^...
Text Solution
|
- Two curves C(1)equiv[f(y)]^(2//3)+[f(x)]^(1//3)=0 and C(2)equiv[f(y)]^...
Text Solution
|
- The area bounded by the curve y^(2)(2-x)=x^(3) and x=2 is
Text Solution
|
- Consider the two curves C(1):y=1+cos x and C(2): y=1 + cos (x-alpha)" ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two curves C1: y=1/x a n dC2: y=logx on the x y plane. Let D1...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the function defined implicity by the equation y^(2)-2ye^(sin...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the function defined implicity by the equation y^(2)-2ye^(sin...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two functions f(x)={([x]",",-2le x le -1),(|x|+1",",-1 lt x...
Text Solution
|
- Computing area with parametrically represented boundaries : If the bou...
Text Solution
|
- Computing area with parametrically represented boundaries : If the bou...
Text Solution
|
- Computing area with parametrically represented boundaries : If the bou...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x) be a continuous function fiven by f(x)={(2x",", |x|le1),(x^(2...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x) be continuous function given by f(x)={2x ,|x|lt=1and x^2+a x+...
Text Solution
|