Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- show that the area of the triangle inscribed in the circle x^(2)/a^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Two triangle ABC and D B C lie on the same side of the base B C . From...
Text Solution
|
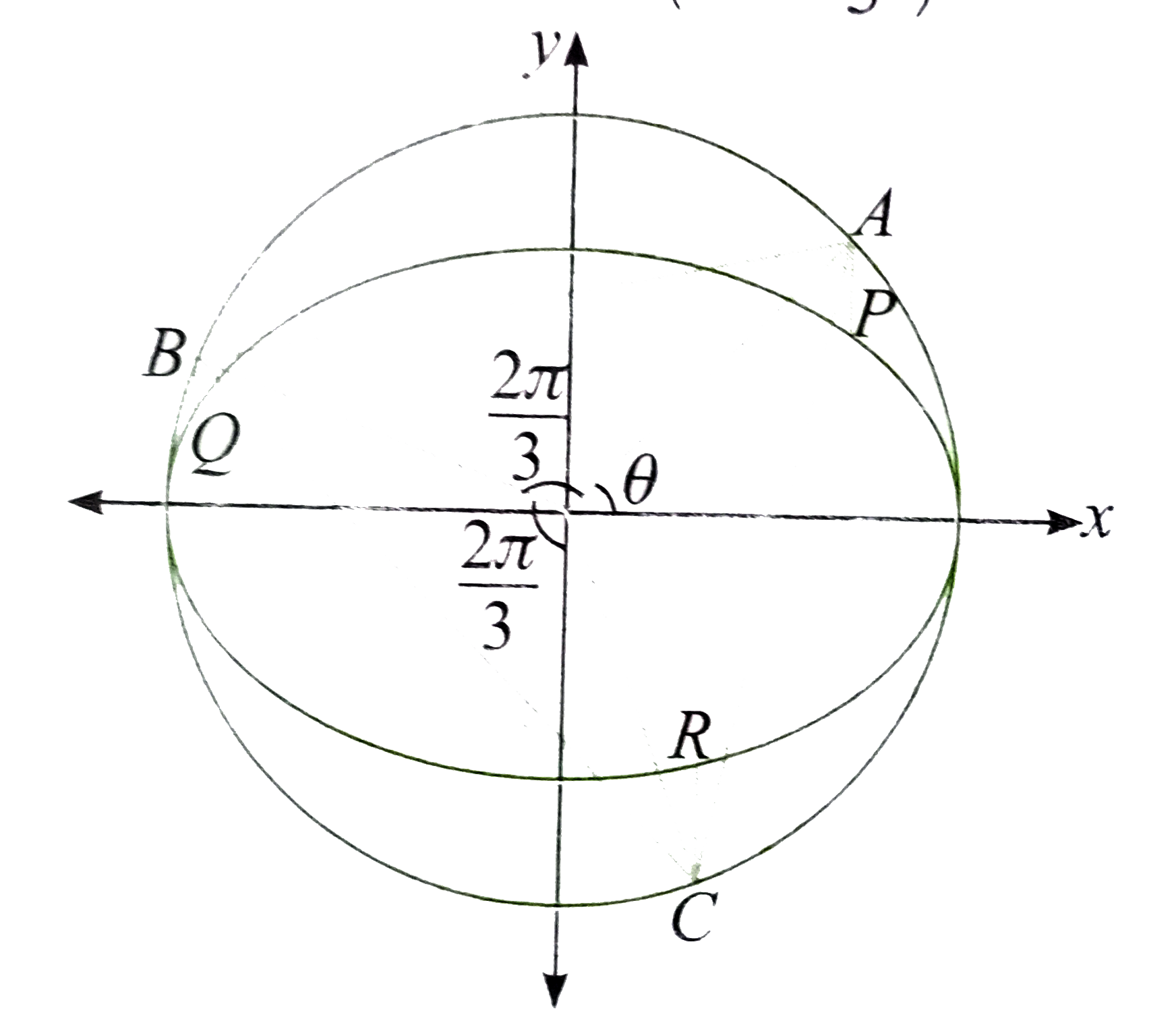
- If P Q R is an equilateral triangle inscribed in the auxiliary circle ...
Text Solution
|
- Let P be a point on the ellipse x^2/a^2+y^2/b^2=1 , 0 < b < a and let ...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABC be an equilateral triangle inscribed in the circle x^2+y^2=a^2...
Text Solution
|
- A normal inclined at 45^@ to the axis of the ellipse x^2 /a^2 + y^2 / ...
Text Solution
|
- If normal at any poin P on the ellipse (x^(2))/(a^(2))+(y^(2))/(b^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- The chord of contact of tangents from three points P, Q, R to the circ...
Text Solution
|
- If P Q R is an equilateral triangle inscribed in the auxiliary circle ...
Text Solution
|