Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
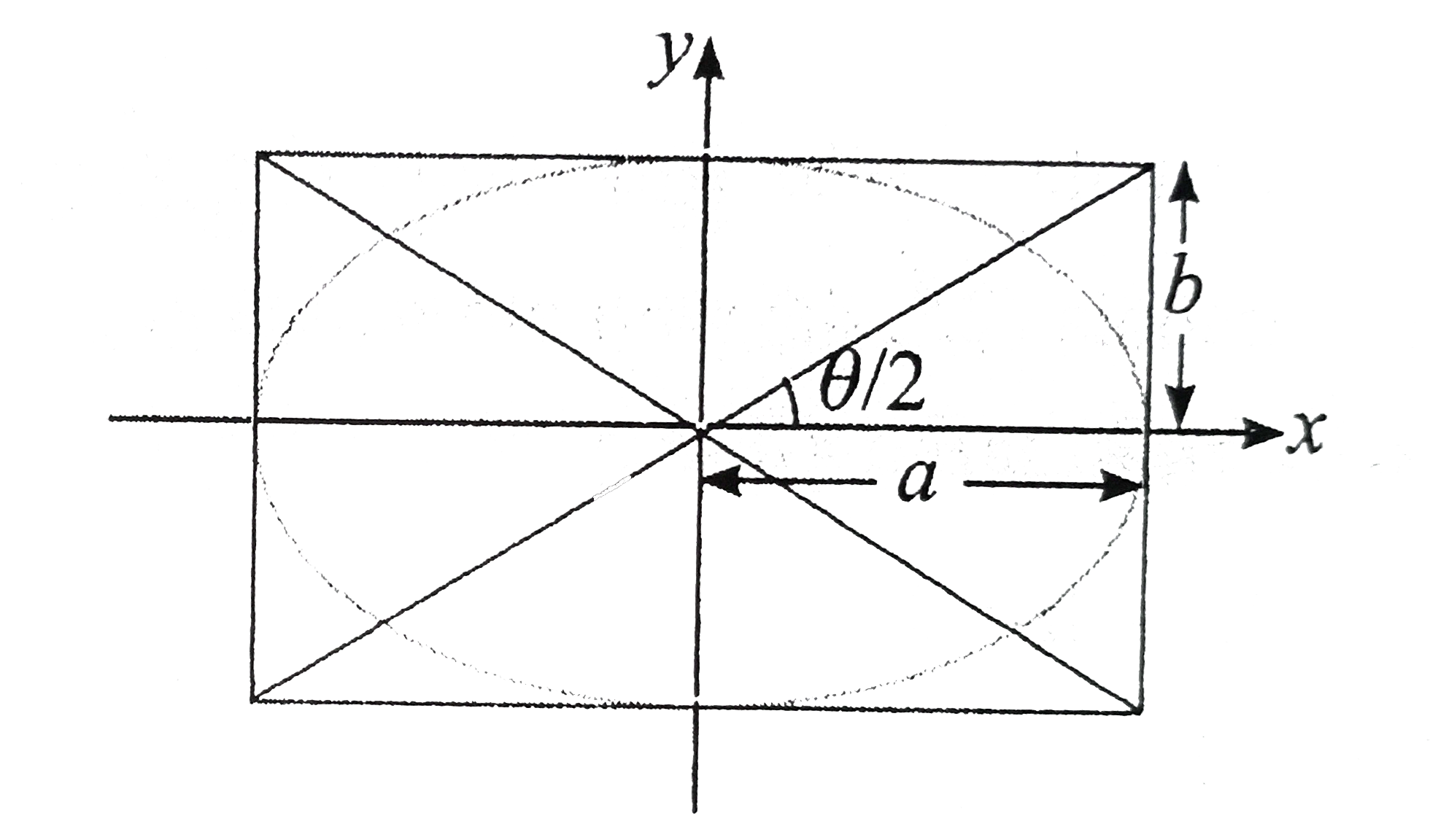
- An ellipse is inscribed in a reactangle and the angle between the diag...
Text Solution
|
- An ellipse is inscribed in a reactangle and the angle between the diag...
Text Solution
|
- Find the length of a diagonal of reactangle whose adjacent sides are 3...
Text Solution
|
- Maximum area of a reactangle which can be inscribed in a circle of a...
Text Solution
|
- An ellipse (x^(2))/(a^(2))+(y^(2))/(b^(2))=1(agtb) is inscribed in a ...
Text Solution
|
- If the ecentricity of the ellipse (x^(2))/( a^(2) +1) +(y^(2))/(a^(2)+...
Text Solution
|
- An ellipse is incribed in a rectangle and if the angle between the dia...
Text Solution
|
- An ellipse is inscribed in a reactangle and the angle between the diag...
Text Solution
|
- The length of a rod is 56 centimetres. It is bent into a reactangle. ...
Text Solution
|