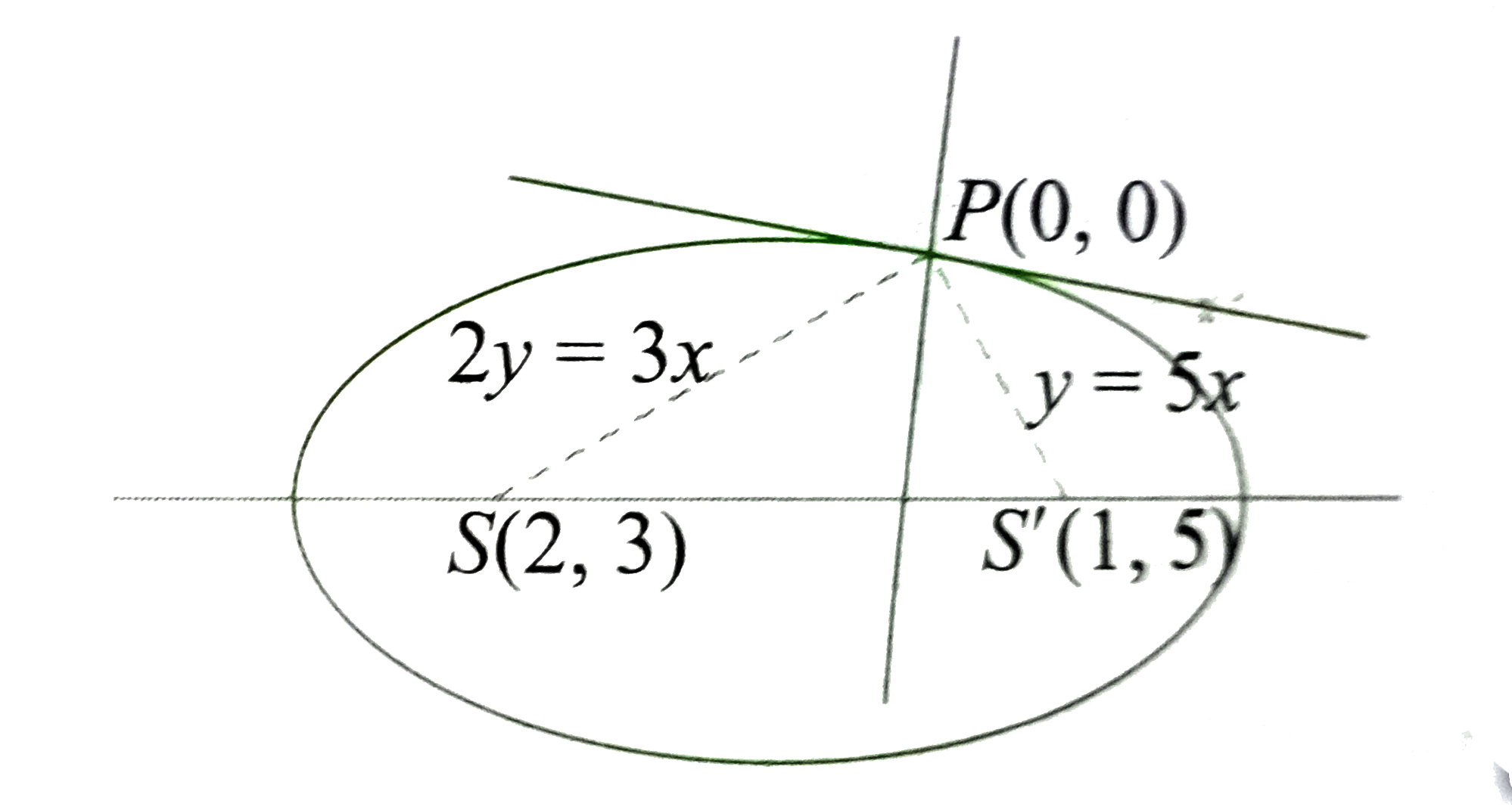A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The coordinates (2, 3) and (1, 5) are the foci of an ellipse which ...
Text Solution
|
- Factorize : 2sqrt(2)x^3+3sqrt(3)y^3+sqrt(5)(5-3sqrt(6)x y)
Text Solution
|
- The coordinates (2, 3) and (1, 5) are the foci of an ellipse which ...
Text Solution
|
- Rationalize the denominator of (2sqrt(5)+3sqrt(2))/(2sqrt(5)-3sqrt(2))
Text Solution
|
- The complex numbrs x and y such that x,x+2y,2x+y are n A.P. and (y+1)^...
Text Solution
|
- If pair of tangents are drawn to the ellipse x^2/16 + y^2/9 = 1 from a...
Text Solution
|
- निम्न में से प्रत्येक को परिमेय हर के रूप में व्यक्त कीजिए - (2sqrt(5)...
Text Solution
|
- Simpilfy (2sqrt(5) + 3sqrt(2))^(2)
Text Solution
|
- गुणनखण्ड कीजिए: 2sqrt(2)x^(3)+3sqrt(3)y^(3)+sqrt(5)(5-3sqrt(6)xy))
Text Solution
|