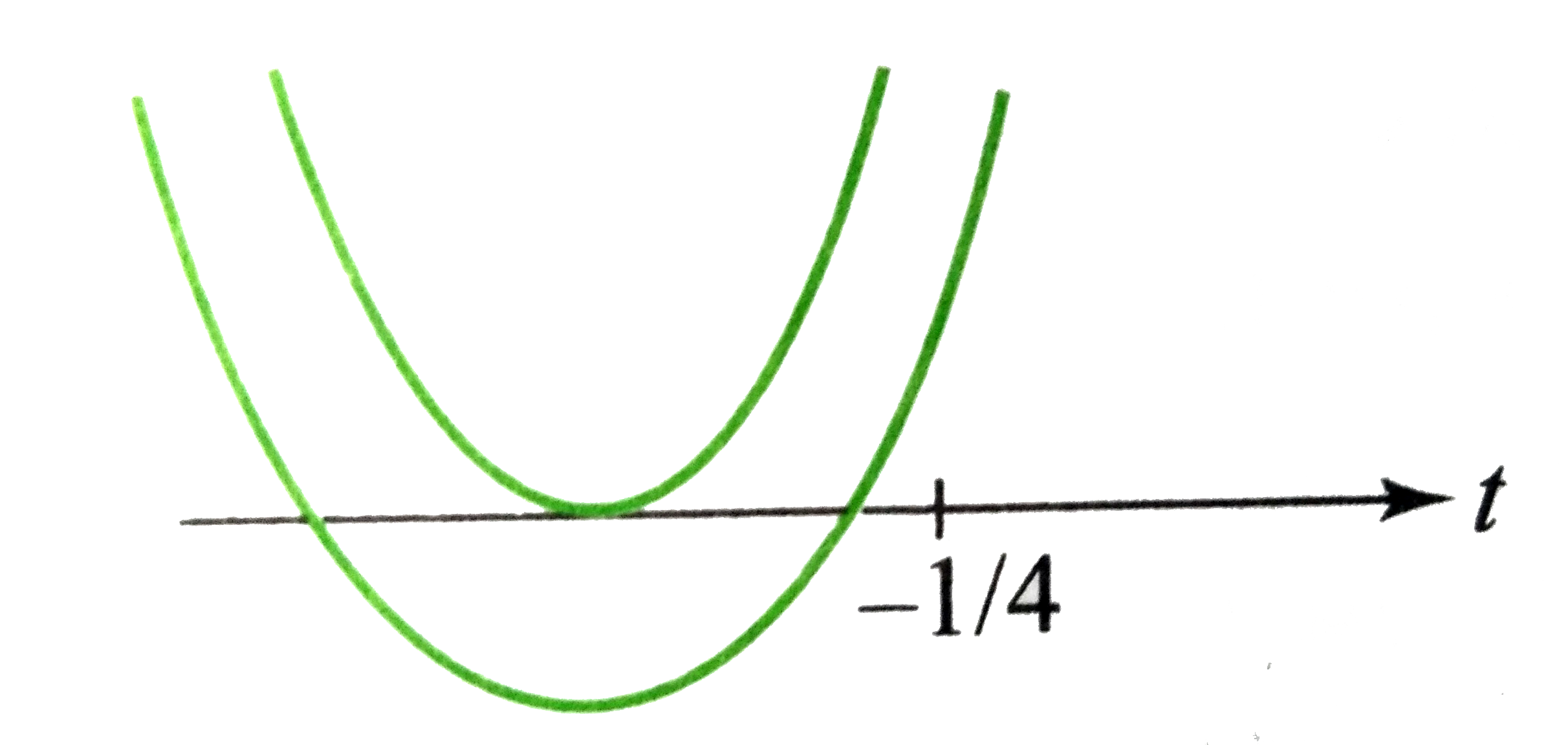
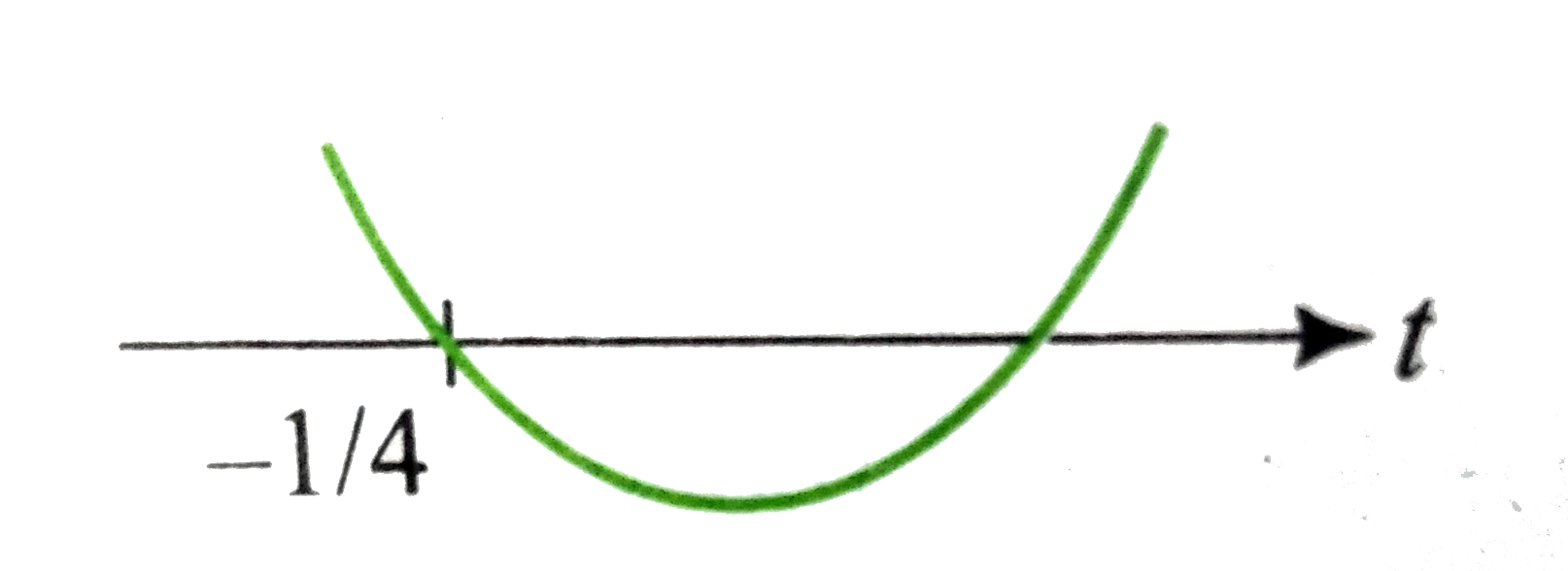
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE|43 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Archives JEE MAIN (single correct Answer Type )|7 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise Linked Comprechension Type|37 VideosSTRAIGHT LINES
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise ARCHIVES (NUMERICAL VALUE TYPE)|1 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
CENGAGE PUBLICATION|Exercise All Questions|291 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PUBLICATION-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-MATRIX MATCH TYPE
- Match the following for the equation x^(2)+a|x|+1=0 where, a is a para...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following for lists:
Text Solution
|
- Match the following lists:
Text Solution
|
- Consider equation ((x^(2)+x)^2)+a(x^(2)+x)+4=0 Match the values of a ...
Text Solution
|
- If ax^(2)+bx+c =0 where ane0 is satisfied by alpha,beta,alpha^(2)andbe...
Text Solution
|
- Consider equation x^(4)-6x^(3)+8x^(2)+4ax-4a^(2)=0,ainR. Then match th...
Text Solution
|