A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
POLYGONS AND QUADRILATERALS
S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT SHEET - 23 |10 VideosPOLYGONS AND QUADRILATERALS
S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT SHEET - 23 |10 VideosPERCENTAGE AND ITS APPLICATIONS
S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise SELFT ASSESMENT SHEET (SECTION-C DISCOUNT )|10 VideosPROBABILITY
S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT SHEET -29 |10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
S CHAND IIT JEE FOUNDATION-POLYGONS AND QUADRILATERALS -QUESTION BANK - 23
- If one side of a regular polygon with seven sides is produced, the ext...
Text Solution
|
- How many sides does a regular polygon have, whose interior angle is ei...
Text Solution
|
- Any cyclic parallelogram having unequal adjacent sides is necessarily ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. The quadrilateral PQRS i...
Text Solution
|
- If angles A, B, C and D of the quadrilateral ABCD, taken in order are ...
Text Solution
|
- The figure formed by joining the mid-points of adjacent sides of a rho...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a rectangle. Find x.
Text Solution
|
- PQRS is a parallelogram. Then y equals.
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a rhombus. angle DAB = 2x + 15^(@), angle DCB = 3x - 30^(@), a...
Text Solution
|
- PQRS is a kite. angle P = 70^(@), angle S = 90.5^(@), angle R equals
Text Solution
|
- If the bisector of the angles A and B of a quadrilateral ABCD meet at ...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a rectangle with angle BAC = 48^(@). Then angle DBC equals
Text Solution
|
- In a trapezium ABCD, AB||DC, AB = AD, angle ADC = 64^(@) and angle BCD...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a square, BA = BQ, QRC and BPD are straight lines and angle PB...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram, ABD and BCD are isosceles triangles, where AB = BC = B...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram, CDP is a straight line, Delta AQD is equilateral angle...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, PQRS is a parallelogram and angle SPQ = 60^(@). I...
Text Solution
|
- In the given diagram, ABCD is a square and Delta BCT is an equilateral...
Text Solution
|
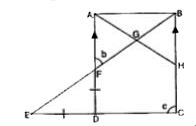
- In the given figure, AD||BC, angle AFG = b and angle BCD = c. Express ...
Text Solution
|
- If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4:7:7, then what type of ...
Text Solution
|