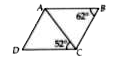
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
UNDERSTANDING QUADRILATERALS
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise EXERCISE(MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION LEVEL-2)|13 VideosUNDERSTANDING QUADRILATERALS
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise EXERCISE(MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION LEVEL-2 MATCH THE FOLLOWING)|1 VideosUNDERSTANDING QUADRILATERALS
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise NCERT SECTION (EXERCISE 3.4)|19 VideosSQUARES AND SQUARE ROOTS
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise Olympiad/HOTS Corner|20 VideosVISUALISING SOLID SHAPES
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise OLYMPIAD/HOTS CORNER|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION-UNDERSTANDING QUADRILATERALS-EXERCISE(MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION LEVEL-1)
- Two adjacent angles of a parallelograms are (2x+25)^@ and (3x-5)^@ . ...
Text Solution
|
- The diagonals do not necessarily intersect at right angles in a
Text Solution
|
- In the given quadrilateral ABCD (not drawn to scale) BC=AC=AD. Find th...
Text Solution
|
- If an angle of a parallelogram is two-thirds of its adjacent angle, th...
Text Solution
|
- The diagonals do not necessarily bisect the interior angles at the ver...
Text Solution
|
- In a square ABCD, AB=(2x+3) cm and BC=(3x-5) cm . Then , the value of ...
Text Solution
|
- State whether the statements are true (T) or (F) false. A quadrilate...
Text Solution
|
- An isosceles trapezium has
Text Solution
|
- The quadrilateral in which only one pair of opposite sides are paralle...
Text Solution
|
- A quadrilateral, which is both a rectangle and a rhombus is a
Text Solution
|
- Adjacent angles of a parallelogram are .
Text Solution
|
- A regular polygon is a polygon whose all sides are equal and all are ...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram if each angle is equal then it is called a
Text Solution
|
- The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 : 4. The smal...
Text Solution
|
- Three angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 1:5:6. The mean of th...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABC is a parallelogram. The /ABD is
Text Solution
|
- The sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is
Text Solution
|
- If PQRS is a parallelogram, then angleP – angleR is equal to
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is a false statement for a parallelogram?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are true for a rectangle? It has ...
Text Solution
|