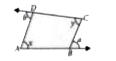
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
UNDERSTANDING QUADRILATERALS
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise EXERCISE(MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION LEVEL-2 SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS)|35 VideosSQUARES AND SQUARE ROOTS
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise Olympiad/HOTS Corner|20 VideosVISUALISING SOLID SHAPES
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise OLYMPIAD/HOTS CORNER|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MTG IIT JEE FOUNDATION-UNDERSTANDING QUADRILATERALS-OLYMPAID/HOTS CORNER
- If ABCD is a parallelogram DeltaADN and DeltaABC are isosceles triangl...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure DO and CO are the bisectors of /ADC and /BCD respe...
Text Solution
|
- The diagonals of a rectangle A B C D meet at Odot If /B O C=44^0, find...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a square of area of 4 square units which is divided into 4 non...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure (not drawn to scale), ABCD is a parallelogram and ...
Text Solution
|
- The measures of the five angles of a hexagon are equal and the sixth a...
Text Solution
|
- If the given figure is made up of 3 identical regular polygons, then f...
Text Solution
|
- Sides AB and CD of a quadrilateral ABCD are extended as shown in the f...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure ABCD is a parallelogram. Then the values of x and ...
Text Solution
|
- in the figure, X is a point in the interior of square ABCD. AXYZ is al...
Text Solution
|