Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HEAT AND TEMPERATURE
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise CONSOLIDATED EXERCISE (Multiple Choice Questions with one or More than One Correct Answer)|4 VideosHEAT AND TEMPERATURE
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise CHALLENGING EXERCISE|5 VideosHEAT AND TEMPERATURE
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise MANDATORY EXERCISE (Exercise Set III)|29 VideosHEAT AND MECHANICAL ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Olympiad and NTSE Level Exercises|7 VideosLASERS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise OLYMPIAD AND NTSE LEVEL EXERCISES |1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-HEAT AND TEMPERATURE -CONSOLIDATED EXERCISE
- The oceans are the reservoir from which water (1) into the atmosphere...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following:
Text Solution
|
- Rankine scale is a temperature scale which takes the absolute zero of ...
Text Solution
|
- Rankine scale is a temperature scale which takes the absolute zero of ...
Text Solution
|
- Rankine scale is a temperature scale which takes the absolute zero of ...
Text Solution
|
- Rankine scale is a temperature scale which takes the absolute zero of ...
Text Solution
|
- Rankine scale is a temperature scale which takes the absolute zero of ...
Text Solution
|
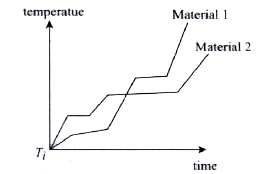
- Two solid blocks having same mass but different material are supplied ...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid blocks having same mass but different material are supplied ...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid blocks having same mass but different material are supplied ...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid blocks having same mass but different material are supplied ...
Text Solution
|
- Two solid blocks having same mass but different material are supplied ...
Text Solution
|