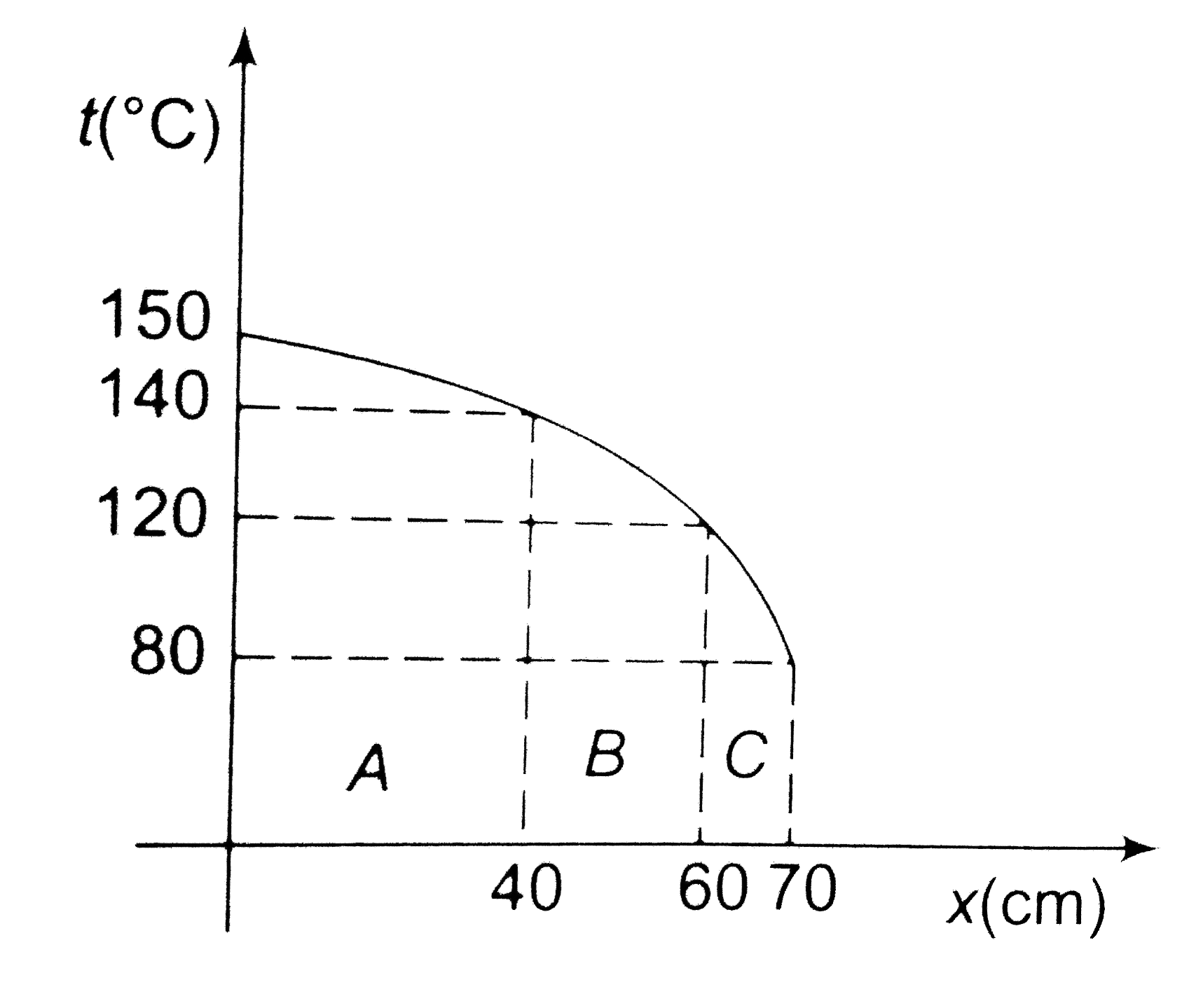
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-TRANSFER OF HEAT-OLYMPIAD AND NTSE LEVEL EXERCISES
- Two ends of a conducting rod of varying cross-section are maintained a...
Text Solution
|
- The graph shown gives the temperature along an X axis that extends dir...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : While measuring the thermal conductivity of liquid experim...
Text Solution
|
- Heat travels through vaccum by
Text Solution
|
- We consider the radiation emitted by the human body. Which of the foll...
Text Solution
|
- When we rub our palms they get heated but to a maximum temperature bec...
Text Solution
|
- In conduction process, the molecules of the solid pass the heat from o...
Text Solution
|
- Solids are not heated by convection because
Text Solution
|
- A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice cream. Its other end
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Temperature near the sea-coast are moderate. Reason : Wa...
Text Solution
|