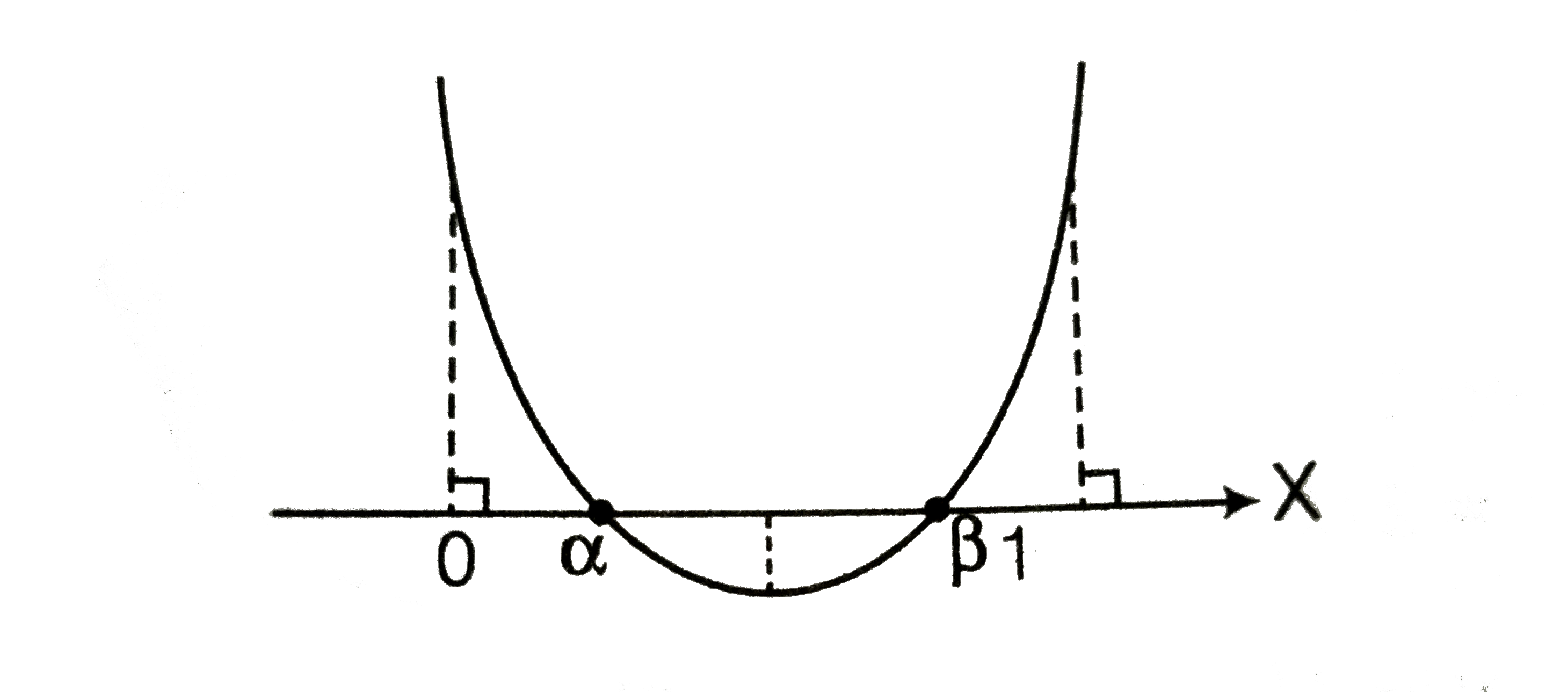
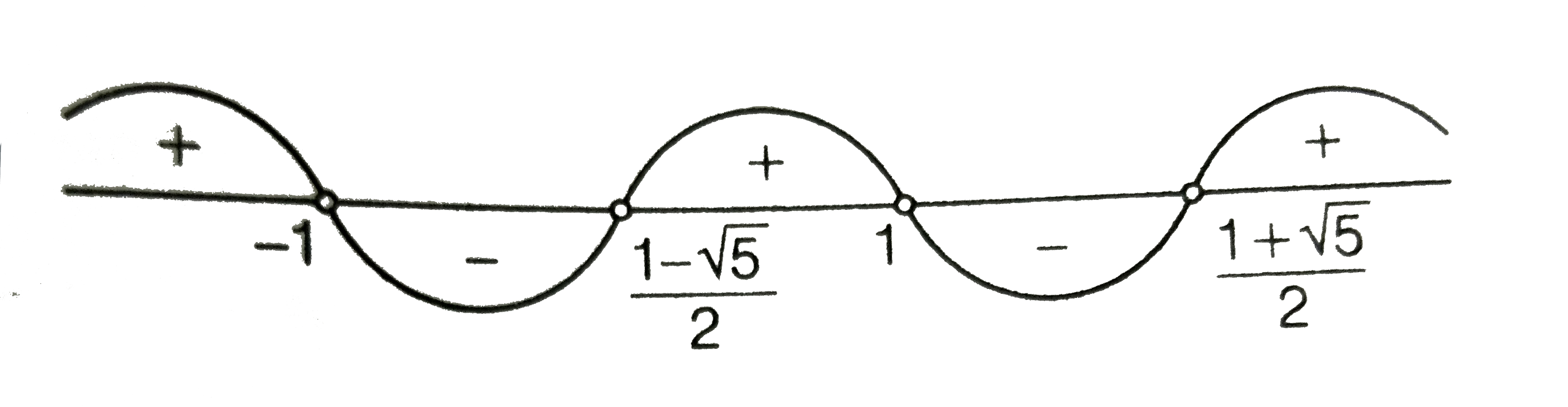
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THEORY OF EQUATIONS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise SCQ_TYPE|1 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (More Than One Correct Option Type Questions)|15 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise For Session 5|10 VideosTHE STRAIGHT LINES
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise The Straight Lines Exercise 8 : (Questions Asked in Previous 13 years Exams)|1 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL COORDINATE SYSTEM
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Three Dimensional Coordinate System Exercise 12 : Question Asked in Previous Years Exam|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT MATHS-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-Exercise (Single Option Correct Type Questions)
- If x(1) and x(2) are the arithmetic and harmonic means of the roots fo...
Text Solution
|
- If f(x) is a cubic polynomial x^3 + ax^2+ bx + c such that f(x)=0 has ...
Text Solution
|
- The value of the positive integer n for which the quadratic equation s...
Text Solution
|
- If one root of the equation x^(2)-lamdax+12=0 is even prime while x^(2...
Text Solution
|
- Number of real roots of the equation sqrt(x)+sqrt(x-sqrt((1-x)))=1 is
Text Solution
|
- The value of sqrt(7+sqrt(7-sqrt(7+sqrt(7-….)))) upto oo is
Text Solution
|
- For any value of x the expression 2(k-x)(x+sqrt(x^2+k^2)) cannot excee...
Text Solution
|
- solve x^2+2x+4 = 0
Text Solution
|
- Let alpha,beta,gamma be the roots of (x-a) (x-b) (x-c) = d, d != 0, th...
Text Solution
|
- If one root fo the quadratic equation ix^(2)-2(i+1)x+(2-i)=0,i=sqrt(-1...
Text Solution
|
- Find the number of solutions of abs([x]-2x)=4, where [x] is the greate...
Text Solution
|
- if x^2+x+1 is a factor of ax^3+bx^2+cx+d then the real root of ax^3+...
Text Solution
|
- THe value of x which satisfy the equation (sqrt(5x^2-8x+3))-sqrt((5x...
Text Solution
|
- the roots of the equation (a+sqrt(b))^(x^2-15)+(a-sqrt(b))^(x^2-15)=2a...
Text Solution
|
- The number of pairs (x,y) which will satisfy the equation x^2-x y+y^2=...
Text Solution
|
- The number of positive integral solutions of x^4-y^4=3789108 is
Text Solution
|
- if x^3+ax+1=0 and x^4+ax^2+1=0 have common root then the exhaustive se...
Text Solution
|
- The value of a for which the equation (1-a^2)x^2+2ax-1=0 has roots bel...
Text Solution
|
- Solution set of x-sqrt(1-|x|)lt0, is
Text Solution
|
- If the quadratic equations, a x^2+2c x+b=0 and a x^2+2b x+c=0(b!=c) ha...
Text Solution
|