A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THEORY OF EQUATIONS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Single Integer Answer Type Questions)|10 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Matching Type Questions)|2 VideosTHEORY OF EQUATIONS
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (More Than One Correct Option Type Questions)|15 VideosTHE STRAIGHT LINES
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise The Straight Lines Exercise 8 : (Questions Asked in Previous 13 years Exams)|1 VideosTHREE DIMENSIONAL COORDINATE SYSTEM
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Three Dimensional Coordinate System Exercise 12 : Question Asked in Previous Years Exam|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT MATHS-THEORY OF EQUATIONS-Exercise (Passage Based Questions)
- If G and L are the greatest and least values of the expression(2x^(2)-...
Text Solution
|
- If G and L are the greatest and least values of the expression(2x^(2)-...
Text Solution
|
- If roots of the equations x^(4)-12x^(3)+cx^(2)+dx+81=0 are positive. ...
Text Solution
|
- If the roots of the equaion x^4-12 x^3+c x^2+dx+81=0 are positive then...
Text Solution
|
- If roots of the equations x^(4)-12x^(3)+cx^(2)+dx+81=0 are positive. ...
Text Solution
|
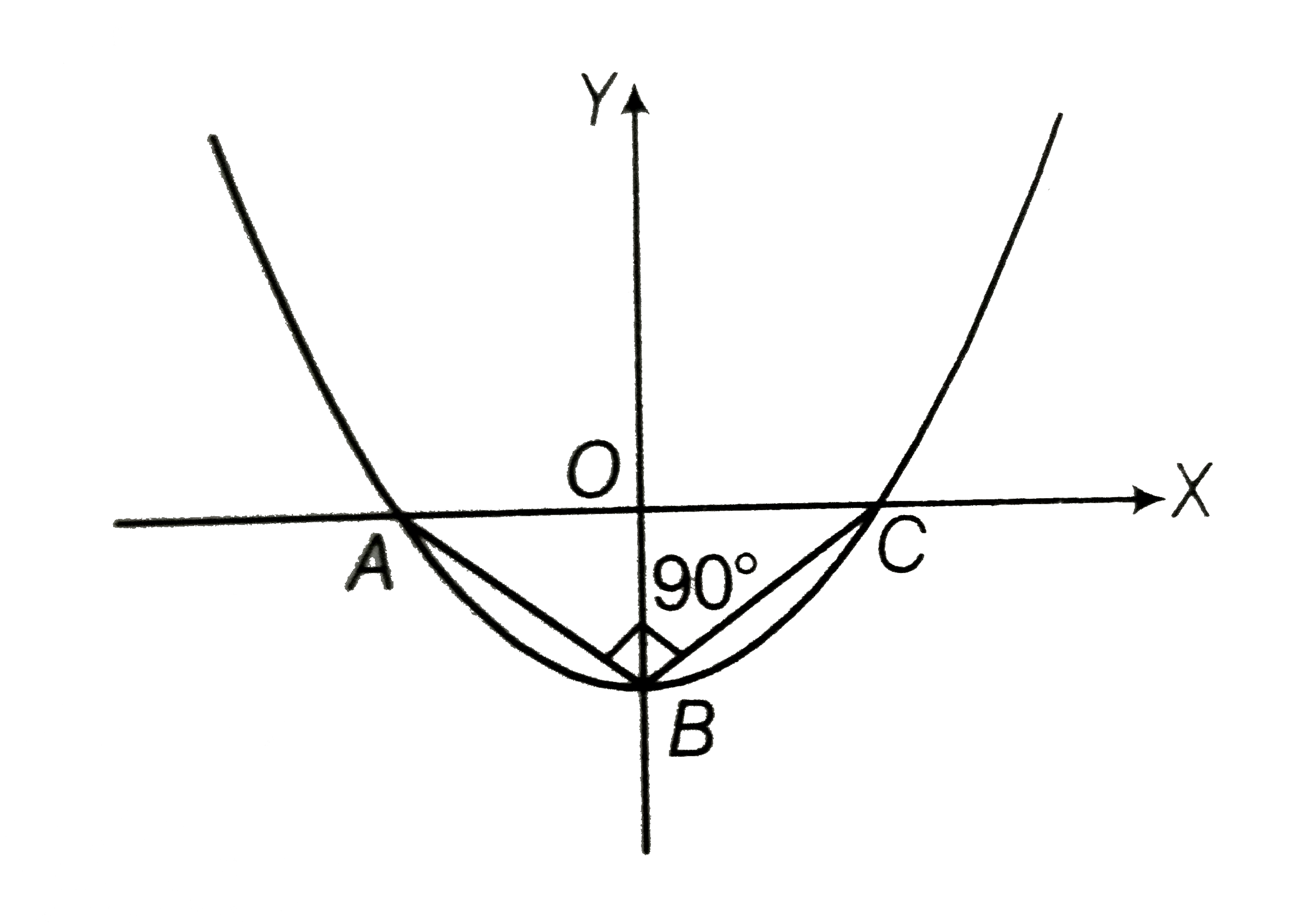
- In the given figue vertices of DeltaABC lie on y=f(x)=ax^(2)+bx+c. The...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure vertices of DeltaABC lie on y=f(x)=ax^(2)+bx+c. Th...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figue vertices of DeltaABC lie on y=f(x)=ax^(2)+bx+c. The...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x) = x^2 + b1x + c1. g(x) = x^2 + b2x + c2. Real roots of f(x)...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x) = x^2 + b1x + c1. g(x) = x^2 + b2x + c2. Real roots of f(x)...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)=x^(2)+bx+c and g(x)=x^(2)+b(1)x+c(1) Let the real roots of f...
Text Solution
|
- If ax^2-bx + c=0 have two distinct roots lying in the interval (0,1); ...
Text Solution
|
- If ax^(2)+bx+c=0 have two distinct roots lying in the interval (0,1),a...
Text Solution
|
- If ax^(2)-bx+c=0 have two distinct roots lying in the interval (0,1),a...
Text Solution
|
- If 2x^(3)+ax^(2)+bx+4=0 (a and b are positive real numbers) has three ...
Text Solution
|
- If 2x^(3)+ax^(2)+bx+4=0 (a and b are positive real numbers) has three ...
Text Solution
|
- If 2x^(3)+ax^(2)+bx+4=0 (a and b are positive real numbers) has three ...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha, beta, gamma , delta are the roots of the equation x^(4)+Ax^(...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha, beta, gamma, delta are the roots of the equation x^(4)+Ax^(3...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha, beta, gamma, delta are the roots of the equation x^(4)+Ax^(3...
Text Solution
|