Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
VECTOR ALGEBRA
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise VECTOR ALGEBRA EXERCISES 1: Single Option Correct Type Questions|1 VideosVECTOR ALGEBRA
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (More Than One Correct Option Type Questions)|7 VideosVECTOR ALGEBRA
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise For Session 3|11 VideosTRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS AND IDENTITIES
ARIHANT MATHS|Exercise Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT MATHS-VECTOR ALGEBRA-Exercise (Single Option Correct Type Questions)
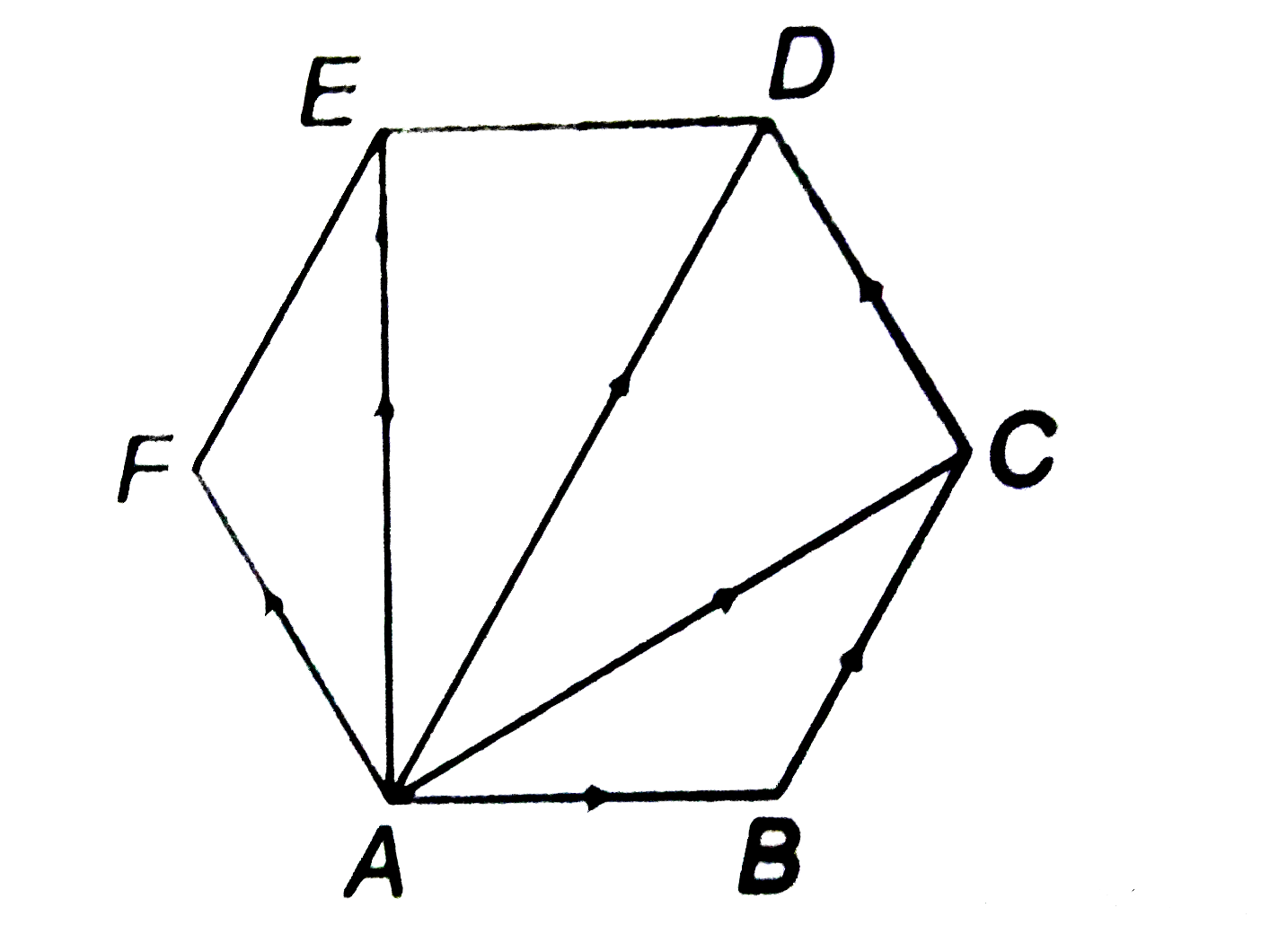
- If ABCDEF is a regular hexagon then vec(AD)+vec(EB)+vec(FC) equals :
Text Solution
|
- Find the discriminant of the quadratic equation x^2+3x+2
Text Solution
|
- In a regular hexagon ABCDEF, prove that AB+AC+AD+AE+AF=3AD.
Text Solution
|
- Find the dot product of the vector 2hati+3hatj+1hatk and 1hati+2hatj+3...
Text Solution
|
- If a and b are two non-zero and non-collinear vectors then a+b and a-b...
Text Solution
|
- If |veca+ vecb| lt | veca- vecb|, then the angle between veca and vecb...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitudes of mutually perpendicular forces a,b and c are 2,10 and...
Text Solution
|
- If hati-3hatj+5hatk bisects the angle between hata and -hati+2hatj+2ha...
Text Solution
|
- Find the discriminant of the quadratic equation x^2+5x+4=0 and also fi...
Text Solution
|
- Given three vectors vec a=6 hat i-3 hat j , vec b=2 hat i-6 hat ja ...
Text Solution
|
- ' I ' is the incentre of triangle A B C whose corresponding sides are ...
Text Solution
|
- If vecx and vecy are two non-collinear vectors and ABC is a triangle w...
Text Solution
|
- If vec xa n d vec y are two non-collinear vectors and a, b, and c r...
Text Solution
|
- If the resultant of two forces is equal in magnitude to one of the ...
Text Solution
|
- If vec b is a vector whose initial point divides the join of 5 hat ...
Text Solution
|
- find the term independent of x in the expansion of (2x-1/x)^2 ?
Text Solution
|
- If veca and vecb are two unit vectors and theta is the angle between t...
Text Solution
|
- A, B, C and D have position vectors veca, vecb, vecc and vecd, repecti...
Text Solution
|
- if alpha and beta are the root of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x^2-...
Text Solution
|
- If a +b+c = alphad, b+c+d=beta a and a, b, c are non-coplanar, then t...
Text Solution
|