A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JBD PUBLICATION-LAWS OF MOTION-EXAMPLE
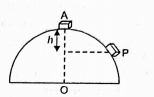
- A small body of mass m slides down from the top of a frictionless hemi...
Text Solution
|
- Give one example each of position depedent force
Text Solution
|
- Give one example each of time dependent force.
Text Solution
|
- Give one example each of constant force
Text Solution
|
- Give one example each of velocity dependent force.
Text Solution
|
- Does equilibrium mean that a body is at rest?
Text Solution
|
- Why do we prefer a heavy hammer to drive a nail into wood?
Text Solution
|
- Action and reaction forces do not balance each other. Why?
Text Solution
|
- What is the principle of working of a rocket?
Text Solution
|
- What is the measure of inertia of a body?
Text Solution
|
- A meteorite burns in the atmosphere before it reaches the earth's surf...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relation beteen coefficient fo friction and angle of frict...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relation between coefficient of friction and angle of repo...
Text Solution
|
- What are the methods of reducing friction?/
Text Solution
|
- The angle of friction betwen two surfaces is 30^@ ,what is coefficien...
Text Solution
|
- What type of friction is involved when axle rotates in a wheel?
Text Solution
|
- Arrange mus, muk and mur in descending order.
Text Solution
|
- We slip easily on a rainy day because coefficient of friction
Text Solution
|
- Why are ruber tyres preffered to iron tyres?
Text Solution
|
- Why are aeroplanes given conical shape?
Text Solution
|
- Define coefficient of friction.
Text Solution
|
 .
.