Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HUMAN REPRODUCTION
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (MOAT EXPECTED QUESTIONS)|3 VideosHUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS)|12 VideosMICROBES IN HUMAN WELFARE
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS)|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-HUMAN REPRODUCTION-LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Describe the ultra-structure of human sperm with the help of a labelle...
Text Solution
|
- What is spermatogenesis ? Briefly describe the process of spermatogene...
Text Solution
|
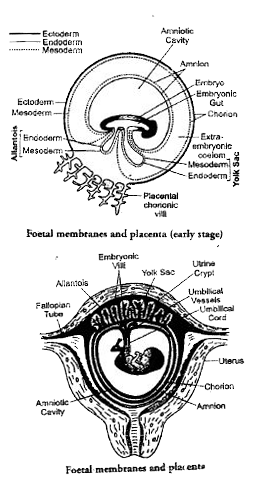
- What are foetal membranes. Give their names. Mention the function of ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe human female reproductive system with labelled diagram.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the role of the following hormones with reference to Menstrual...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the formation and fate of three germlayers inamammalian embry...
Text Solution
|
- At which stage of life does oogenesis begin in human females.
Text Solution
|
- Namethe organ where oogenesis gets completed inhuman females.
Text Solution
|
- Give a schematic representation of oogenesis in human females.
Text Solution
|
- What do you call the area of a human ovum from where the sperm makes t...
Text Solution
|
- Name the enzyme produced by the sperm to facilitate its entry.
Text Solution
|
- Draw a well labelled diagram of structure of Human ovum.
Text Solution
|
- Describe in detail the accessory glands of male and female humanbeing.
Text Solution
|
- What is cleavage ? Write down its characteristics.
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the role of pituitary and the ovarian hormones in menstrual cy...
Text Solution
|
- Write the functions of : Corpus luteum
Text Solution
|
- Write the functions of : Endometrium
Text Solution
|
- Write the functions of : Acrosome.
Text Solution
|
- Write functions of : Sperm tail
Text Solution
|