Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS |31 VideosPRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS |31 VideosPRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES IN BIOTECHNOLOGY
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|16 VideosREPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (5 MARKS)|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION -SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Why are hemophilia and red green color blindness observed usually in m...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the chromosomal theory of linkage.
Text Solution
|
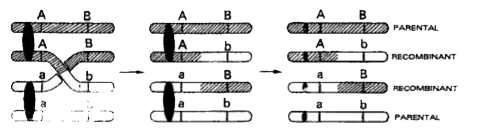
- What is crossing over ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the significance of crossing over and linkage.
Text Solution
|
- What will be the kind of children born to normal father and carrier mo...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the kind of children born to color blind father and carri...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the kind of children born to haemophilic father and carri...
Text Solution
|
- Write the significance of variations.
Text Solution
|
- Define Mendel’s law of segregation. Draw only Punnett’s square to expl...
Text Solution
|
- Define Mendel’s law of dominance. Draw only Punnett’s square to explai...
Text Solution
|
- A haemophilic man marries normal female.Withthe help of a Punnett squa...
Text Solution
|
- What is the cause of phenylketonuria? Write symptoms.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the sex-determination mechanism in humans. How is it different...
Text Solution
|
- Why are Grasshopper.and Drosophila said to show male heterogamety? Exp...
Text Solution
|
- Explain female heterogamety with the help of an example.
Text Solution
|
- Describe Mendelian disorders and mention its two types giving suitable...
Text Solution
|
- If a true breeding homozygous pea plant with green pod and axial flowe...
Text Solution
|
- If a true breeding homozygous pea plant with green pod and axial flowe...
Text Solution
|
- If a true breeding homozygous pea plant with green pod and axial flowe...
Text Solution
|
- Why is thalassaemia categorised as a Mendelian disorder ? Write the sy...
Text Solution
|