Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS |66 VideosPRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES IN BIOTECHNOLOGY
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|16 VideosREPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (5 MARKS)|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATION -LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Define crossing over. Explain its types. Also discuss its mechanism.
Text Solution
|
- Define mutation.
Text Solution
|
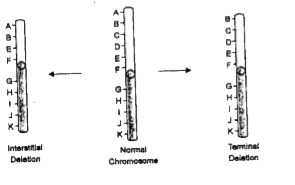
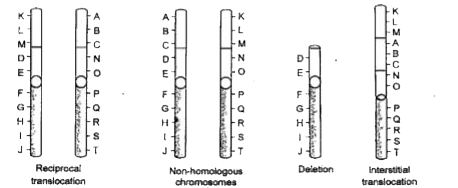
- Describe in detail chromosomal mutations.
Text Solution
|
- Define pleiotropy.Explain pleiotropy with suitable example.
Text Solution
|
- What are induced mutations ? Write about physical and chemical mutagen...
Text Solution
|
- Describe chemical and physical mutagens to bring about mutations.
Text Solution
|
- Define gene mutation
Text Solution
|
- Explain in detail about the types of gene mutations.
Text Solution
|
- Give two reasons why Mendel chose garden pea for his experiments? Give...
Text Solution
|
- List any four symptoms of Down's syndrome. What is the basis of this d...
Text Solution
|
- Study the given pedigree chart and answer the questions that follow. ...
Text Solution
|
- Study the given pedigree chart and answer the questions that follow. ...
Text Solution
|
- Study the given pedigree chart and answer the questions that follow. ...
Text Solution
|
- A dihybrid heterozygous round, yellow seeded garden pea was crossed wi...
Text Solution
|
- A dihybrid heterozygous round, yellow seeded garden pea was crossed wi...
Text Solution
|
- A dihybrid heterozygous round, yellow seeded garden pea was crossed wi...
Text Solution
|
- Study the given pedigree chart and answer the questions that follow. ...
Text Solution
|
- Study the given pedigree chart and answer the questions that follow. ...
Text Solution
|
- Study the given pedigree chart and answer the questions that follow. ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the pattern of inheritance of haemophilia in humans. Why the p...
Text Solution
|