1. Immunodeficiency. Immunodeficiency is an increased susceptibility to infectious diseases due to immune disorder. It is a genetic disorder.
Types. Immunodeficiency may be primary or secondary.
(i) Primary immunodeficiency exists from the birth. A person may lack B-cells. or T-cells, or both from birth. Such a person is highly susceptible to infection. A serious congenital disease, called severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) results from the absence of both B and T-cells. In developed countries, such children have been kept alive in germ-free .isolation suits. similar to space suits. SCID is caused by a defect in the gene that codes for the enzyme adenosine deaminase. Lack of this enzyme makes the body defenseless against infections. SCID is the first genetic disorder to be combated with gene therapy.
(ii) Secondary immunodeficiency occurs in individuals in which originally normal immune system gets impaired due to prolonged illness, malnutrition, radiation and use of certain drugs Hodgkin.s disease and AIDS. are secondary immunodeficiency diseases.
2. AIDS-Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
What is AIDS ? It is a disorder of cell mediated immune system of the body. There is a reduction in the number of helper T cells which stimulate antibody production by B-cells. This results in the loss of natural defence against viral infection.
Discovery. AIDS was first noticed in USA amongst homosexuals in 1981. Virus of AIDS was isolated and identified by Prof Luc Montagnier in France in 1983 and in 1984 by Prof Robert Gallo in USA. The virus of AIDS was officially named Human Immuno deficiency virus (HIV) în 1986 by the International Committee on Viral Nomenclature. AIDS infections were detected in India for the first time in prostitutes of Chennai in 1986.

The AIDS virus may have passed from a monkey host into human population in Africa during 1960s.
Pathogen (Causative Agent). The virus was identified and named by Americans as HCLV III (Human cell leukemia virus III), but as stated earlier the name of the virus was changed to HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus). HIV is a retrovirus that attacks helper T cells.
Structure of HIV. The virus is spherical with a diameter of about 90-120 nm. Its genome consists of a single-stranded RNA filament segmented into two identical filaments and associated with a reverse transcriptase enzyme. The envelope consists of a lipid bilayer derived from host cell membrane and projecting knob like glycoprotein spikes with pedicles formed of virus coded glycoprotein. It contains two protein coats.
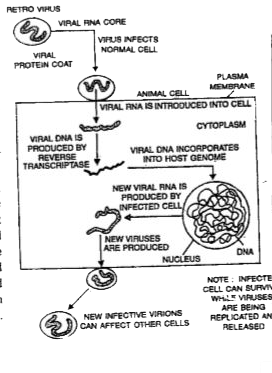
Mode of Action of AIDS Virus. After the entrance of the virus into the body of the person, the virus enters into macrophages where RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA with the help of reverse transcriptase enzyme. This viral DNA gets incorporated into the host cell.s DNA and directs the infected cells to produce viruses. The macrophages produce virus and act like a HIV factory. Simultaneously HIV virus enters into helper T lymphocytes where it replicates and produces other viruses. This is repeated so that the number of T lymphocytes decreases in the body of the infected person. During this period, the infected person suffers from fever, diarrhoea and weight loss. Since the number of helper T lymphocytes decreases in the body, the person starts suffering from infections of bacteria especially Mycobaclerium, viruses, fungi and even parasites like Toxo- plasma. The patient gets immune deficiency and he/she is unable to protect `"himself"//"herself"` against these infections.
Transmission. Virus of AIDS is transmitted via blood and semen, (i) Transfusion of infected blood or blood products, (ii) Use of contaminated needles and snnges to inject drugs or vaccines, (iii) Use of contaminated razors. (iv) Use of contaminated needles for boring pinnae, (v) Sexual intercourse with an infected partner without a condom, (vi) From infected mother to child through placenta, (vii) Artificial insemination, (viii) Organ transplant. AIDS Cannot be aquired by the following : (i) Insect bites, (ii) Crowded transport, (iii) Shaking hands, (iv) Sharing towels, (v) Coughing and sneezing, (vii) Kissing and embracing, (vii) Sharing utilities and telephone, (viii) Swimming pools and toilets.
Incubation period. The incubation period of AIDS ranges between 6 months to 10 years.
Symptoms. The symptoms of HIV infection include fever, lethargy, pharyngitis, nausea, headache, rashes, etc.
Diagnosis. AIDS can be diagnosed by ELISA* test and Western Blotting test. Western blotting test is employed for confirmation of ELISA positive cases.
Treatment. Although there is no cure for AIDS, use of certain drugs can prolong the life of AIDS patient. Zidovudine or AZT (3.- azidoz., 3.-dideoxythymidine) was the first drug used and continues to be the drug of choice for the treatment of AIDS. Didanosine (dldeoxyionosine. DDI) is another drug employed to treat AIDS.
Prevention (Prophylaxis). No vaccine has been prepared so far against AIDS virus. The following steps may help in preventing the AIDS.
(i) People should be educated about AIDS. Ever). year, December 1 is recalled as the World AIDS Day. It is one of the methods to educate the people about AIDS.
(ii) Blood test must be done in blood donors, donors of semen, donors of organs (kidney, lung, liver), patients undergoing haemodialysis, and pregnant women.
(iii) Disposable needles and syringes should be used. Used needles and syringes must be destroyed.
(iv) in sexual relationship one should be monogamous.
(v) Dentists should use sterilized equipments.
(vi) Avoid tatoos, ear and nose piercing from unqualified people.
(vii) Avoid use of common blades in btuber.s shop.
Many people are ignorant about AIDS and it has been said that "don.t die of ignorance". NACO (National AIDS control organization) and other NGOs (Non-government of organisations) are doing good work to educate people about AIDS.
AIDS-Related Complex (ARC). It is miU form of AIDS. Its symptoms are swollen lymph nodes, fever, sweating at night and weight loss. Patients with ARC have a high possibility of early development of AIDS. ARC is also known as prodromal AIDS.

