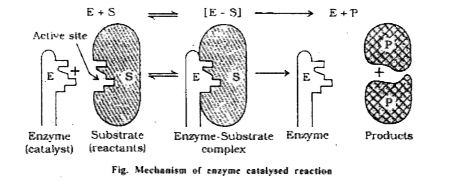
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-SURFACE CHEMISTRY -Question Bank
- How do enzymes differ from catalysts ?
Text Solution
|
- What are Enzymes ? Give important characteristics of enzyme catalysis.
Text Solution
|
- Give the mechanism of heterogeneous catalysed reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Explain two applications of enzymes.
Text Solution
|
- What are colloids ?
Text Solution
|
- which are the properties of colloidal solution ?
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between true solution and colloidal solution?
Text Solution
|
- Give three differences between suspension and colloid solution.
Text Solution
|
- Name the dispersed phase and dispersion mediumin fog.
Text Solution
|
- Comment on the statement that “colloid is not a substance but a state ...
Text Solution
|
- What are lyophilic and lyophobic sols ? Give one example of each. Why ...
Text Solution
|
- What are gels ? Give an example of elastic and non-elastic gel.
Text Solution
|
- How will you differentiate Lyophilic colloids from Lyophobic colloids?
Text Solution
|
- Lyophillic colloids are more stable than lyophobic colloids. Explain.
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between multimolecular and macromolecular collo...
Text Solution
|
- Give three differences between multimolecular colloids and macromolecu...
Text Solution
|
- What are micelles ? Give one example of a micellar system.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the mechanism of the cleansing action of soaps
Text Solution
|
- Discuss cleansing action of soap by micelle formation.
Text Solution
|
- Write short note on peptisation.
Text Solution
|