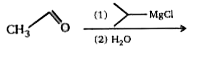
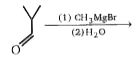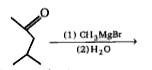A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In which of the following reaction 2^(@) alcohol is obtained as a prod...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reactions wil give 2^(@) chiral alcohol as majo...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following reaction 3^(@) alcohol will be obtained as a...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following reactions, alcohol will be formed as final p...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following reactions 3^(@) alcohol will be obtained as ...
Text Solution
|
- एनीलीन एलोराइड की जलीय KOH से अभिक्रिया द्वारा एलकोहॉल बनती है लेकिन ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reactions will not yield alcohol as the ...
Text Solution
|
- ऐल्किल क्लोराइड्स कि जलीय KOH से क्रिया करने पर ऐल्कोहल प्राप्त होते ह...
Text Solution
|
- Propionic acid and ethyl alcohol gives a products, same product can be...
Text Solution
|