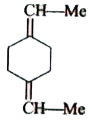
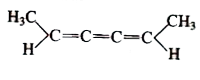
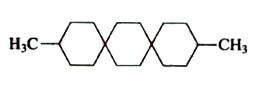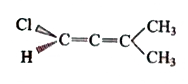A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Which of the following compounds are optically inactive but exhibit ge...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds will exhibits trans (geometrical) iso...
Text Solution
|
- Both geometrical and optical isomerism are exhibited by
Text Solution
|
- Both geometrical and optical isomerism are exhibited by
Text Solution
|
- The complex which exhibits geometrical as well as optical isomerism is...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will exhibit geometrical as well as optical iso...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following complex compound exhibits geometrical isomerism...
Text Solution
|
- The complex which exhibits geometrical as well as optical isomerism is...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will exhibit geometrical as well as optical iso...
Text Solution
|