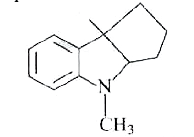
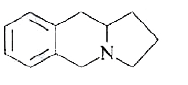
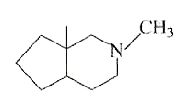
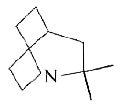
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Only one of the following amines will lose its nitrogen atom as trimet...
Text Solution
|
- Give reason for the following in one or two sectences : 'Dimethyl amin...
Text Solution
|
- Repeated Hofmann elimination reaction (exhaustive methylation followed...
Text Solution
|
- The nitrogan atom in each of the following tertiary amines may be remo...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following in one or two sentences: "Dimethyl amin...
Text Solution
|
- Trimethyl amine has
Text Solution
|
- Nitrogen atom is amines is
Text Solution
|
- Hybridised state of N-atoms in trimethyl amine is
Text Solution
|
- Trimethyl amine on acetylation gives
Text Solution
|