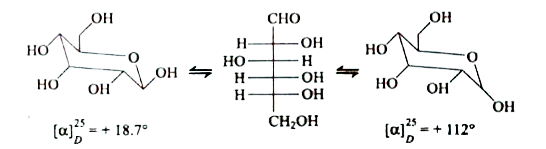
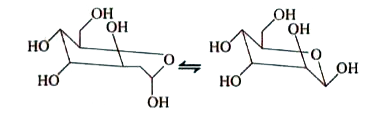
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- D (+) Glucose has melting point 146^@C and specific rotation [alpha](D...
Text Solution
|
- Dextrororatory bytan-2-ol has a specific rotation [alpha](D)^(25) =+13...
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 146^(@)C and specific rotation [alpha](...
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 146^(@)C and specific rotation [alpha](...
Text Solution
|
- The beta and alpha glucose have different specific rotations. When eit...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The specific rotation of a freshly prepared solution of al...
Text Solution
|
- The beta and alpha glucose have different specific rotations. When eit...
Text Solution
|
- alpha-D- ग्लूकोस का विशेष घूर्णक कोण कितना है ?
Text Solution
|
- alpha-D-ग्लूकोस तथा beta-D-ग्लूकोस के विशिष्ट घूर्णन का मान बताइए।
Text Solution
|