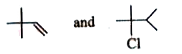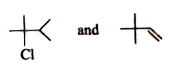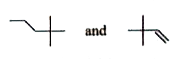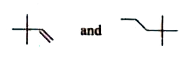To solve the problem, we will analyze the sequence of reactions step by step, identifying the structures of compounds A and B.
### Step 1: Identify Compound A
The first reaction involves compound A, which has the molecular formula C₆H₁₂. Since it reacts with HCl to form B (C₆H₁₃Cl), compound A must be an alkene. This is because alkenes can undergo electrophilic addition reactions with HCl, leading to the formation of alkyl halides.
### Step 2: Reaction of A with HCl
When A (an alkene) reacts with HCl, it adds HCl across the double bond. The addition of HCl introduces a chlorine atom and a hydrogen atom to the molecule, resulting in B (C₆H₁₃Cl). The reaction can lead to the formation of two isomers (C and D) due to the possibility of carbocation rearrangement.
### Step 3: Identify Compound B
Since B is an alkyl halide (C₆H₁₃Cl), we can deduce that it is formed from the addition of HCl to A. The structure of B will depend on the position of the double bond in A and the stability of the carbocation formed during the reaction.
### Step 4: Reaction of B with AgNO₃
The next step states that B reacts with AgNO₃ to give a white precipitate. This indicates that B is likely a primary or secondary alkyl halide, as these can react with AgNO₃ to form a precipitate of AgCl.
### Step 5: Identify Compound D
Next, B is treated with alcoholic KOH, leading to compound D, which is an isomer of A. The reaction with alcoholic KOH suggests that D is formed via elimination (dehydrohalogenation), resulting in another alkene.
### Step 6: Ozonolysis of D
Compound D undergoes ozonolysis, yielding compounds E, which gives a positive iodoform test and a negative Fehling's test. This suggests that E is a methyl ketone, as methyl ketones give a positive iodoform test.
### Step 7: Ozonolysis of A
A also undergoes ozonolysis to yield compounds F and G, both of which give a positive Tollen's test. This indicates that F and G are aldehydes or ketones.
### Step 8: Reaction of F and G
Finally, F and G react with concentrated NaOH under heat to produce HCOONa (sodium formate) and an alcohol. This suggests that F and G are likely aldehydes that can undergo a reaction known as the aldol condensation.
### Conclusion
From the analysis, we can conclude that:
- **Compound A** is an alkene (specifically, 2-hexene).
- **Compound B** is the corresponding alkyl halide (specifically, 2-hexyl chloride).
### Final Structures
- **A (C₆H₁₂)**: 2-Hexene
- **B (C₆H₁₃Cl)**: 2-Hexyl chloride