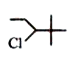
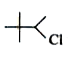
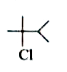
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- From the following sequence of reactions, [A] (C(6)H(12))overset(HCl...
Text Solution
|
- (C(6)H(12))overset(HCl)rarr underset((C(6)H(13)Cl))(B)+(C ) (B)overs...
Text Solution
|
- (A) A(C(7)H(14)) overset(O(3)//Red)(rarr)B(C(3)H(6)O)+C (B) Gives posi...
Text Solution
|
- (A) A(C(7)H(14)) overset(O(3)//Red)(rarr)B(C(3)H(6)O)+C (B) Gives po...
Text Solution
|
- (A) A(C(7)H(14)) overset(O(3)//Red)(rarr)B(C(3)H(6)O)+C (B) Gives po...
Text Solution
|
- (C(6)H(12))overset(HCl)rarr underset((C(6)H(13)Cl))(B)+(C ) (B)overs...
Text Solution
|
- From the following sequence of reactions , [A] (C(6)H(12)) overset(H...
Text Solution
|
- From the following sequence of reactions , [A] (C(6)H(12)) overset(H...
Text Solution
|
- From the following sequence of reactions , [A] (C(6)H(12)) overset(H...
Text Solution
|