Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC CURRENT, RESISTANCE AND E.M.F.
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWERTYPE QUESTIONS |8 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT, RESISTANCE AND E.M.F.
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS|54 VideosELECTRIC CURRENT, RESISTANCE AND E.M.F.
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS |14 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND ELECTROSTATIC FORCE
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS (MOST EXPECTED NUMERICALS )|6 VideosELECTRIC FIELD
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS (MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-ELECTRIC CURRENT, RESISTANCE AND E.M.F.-SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Is a wire carrying current charged?
Text Solution
|
- What is non-ohmic device? Give one example.
Text Solution
|
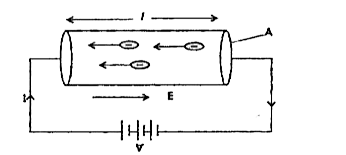
- If the electron drift speed is so small and the electron's charge is s...
Text Solution
|
- A large number of free electrons are present in metals. Why is there n...
Text Solution
|
- Standard resistance coils are made of which materials and why ?
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the effect of temperature on resistivity of metals.
Text Solution
|
- Why conducting wires are made of copper?
Text Solution
|
- What is the resistance of a conductor? State the factors on which resi...
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between e.m.f. and potential diffrence?
Text Solution
|
- What are ohmic and non-ohmic resistors? Give one example of each.
Text Solution
|
- What is e.m.f. of a cell ? On what factors does its value depend ?
Text Solution
|
- Establish the relation between current and drift velocity?
Text Solution
|
- Define drift velocity of electricity and establish its relation with v...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the condition fo rmaximum current through a resisitor, when a n...
Text Solution
|
- Define internal resistance of cell and find an expression for it.
Text Solution
|
- What is internal resistance of a cell? Derive an expression for it.
Text Solution
|
- What is internal resistance of a cell? Derive an expression for it.
Text Solution
|
- The internal resistance of a cell is the resistance of
Text Solution
|
- Derive expression for the total resistance of a circuit in which a few...
Text Solution
|
- Explain colour code for carbon resistors giving examples.
Text Solution
|