Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALCOHOLS , PHENOLS AND ETHERS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise 11. 5 SOME COMMERCIALLY IMPORTANT ALCOHOLS |9 VideosALCOHOLS , PHENOLS AND ETHERS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise 11.6 . ETHERS |8 VideosALCOHOLS , PHENOLS AND ETHERS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise 11 . 4. 2 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES |10 VideosALTERNATING CURRENTS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-ALCOHOLS , PHENOLS AND ETHERS -11. 4 . 3 . CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
- Give two reactions that show acidic nature of phenol Compare -a...
Text Solution
|
- Why alcohols are weaker acids than water ?
Text Solution
|
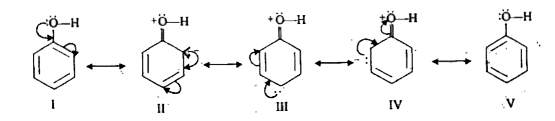
- Explain how does -OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring Acti...
Text Solution
|
- How does the nitration of phenol with dilute nitric acid differ from n...
Text Solution
|
- How will you convert Phenol to Benzoic acid ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following with an example . Kolbe 's reaction .
Text Solution
|
- Explain Reimer Tiemann reaction with one example.
Text Solution
|
- How will you convert phenol into (a) Salicylaldehyde (b) Salic...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the acidic dehydration of alcohols at different temperatures.
Text Solution
|
- Write the reactions of alcohols with : Sodium
Text Solution
|
- How will you convert ethanol to ethane ?
Text Solution
|
- Why phenols are acidic in nature ?
Text Solution
|
- Why Phenols are more acidic than Alcohol ?
Text Solution
|
- Orthonitrophenol and paranitrophenol are more acidic than phenols. Giv...
Text Solution
|
- Alcohols are easily protonated in comparison to phenols.
Text Solution
|
- Why primary alcohols are more acidic than secondary alcohols?
Text Solution
|
- Why -OH group in phenol is ortho and para directing in nature ?
Text Solution
|
- Write the equation of the reaction which takes place when l-propanol i...
Text Solution
|
- Write the following reactions : Phenol with zinc dust.
Text Solution
|
- How Phenol is converted to Benzene ?
Text Solution
|