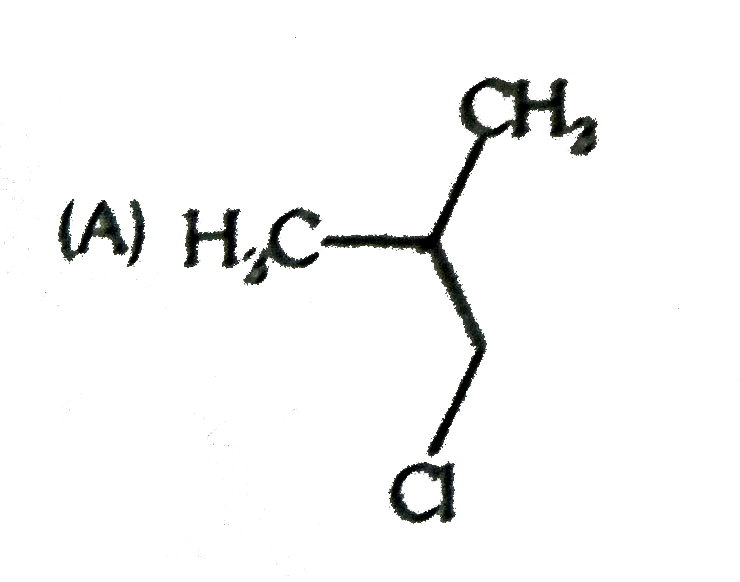
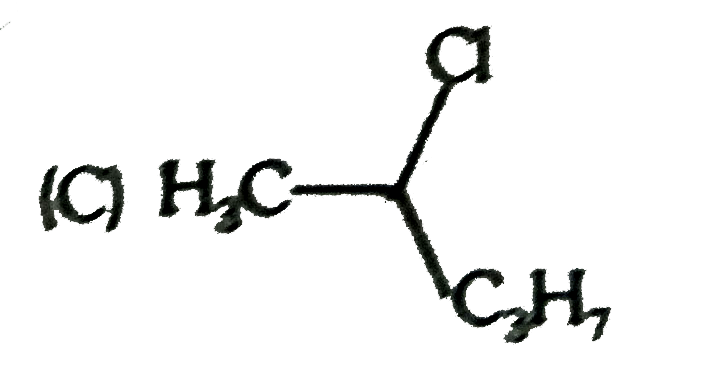
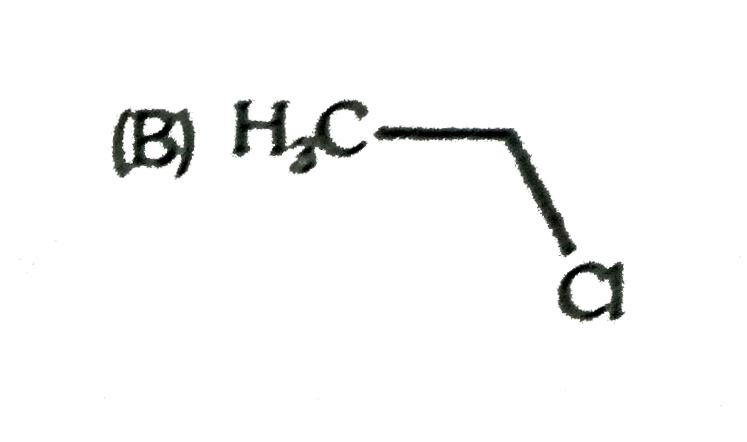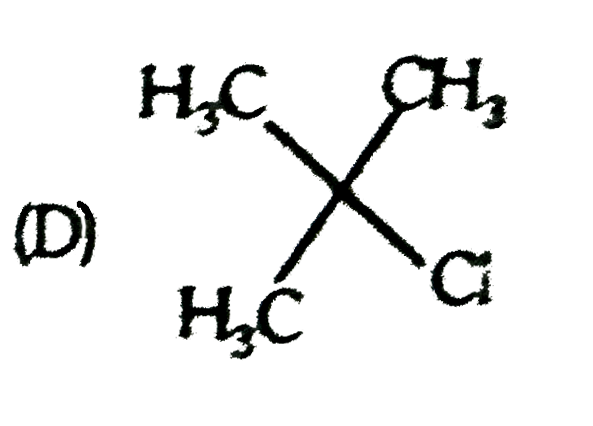A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDE-EXERCISE
- In S(N^(1)) the first step involves the formation of
Text Solution
|
- To form alkane isonitrile, alkyl halide is reacted with:
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following compounds most readily undergoes substituti...
Text Solution
|
- (sec-Butyl bromide) undergoes alkaline hydrolysis by :
Text Solution
|
- Grignard reagent can be prepared by
Text Solution
|
- Most stable carbocation formed from (CH(3))(3)C-Br,(C(6)H(5))(3)CBr,(C...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction
Text Solution
|
- The products of reaction of alcoholic silver nitrite with enthyl bromi...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction , CH(3)Br +OH^(-)rarrCH(3)OH+Br^(-) obeys the mechanism
Text Solution
|
- Ethylidene chloride can be prepared by the reaction of HCl and
Text Solution
|
- 1-phenyl-2-chloropropane on treating with alc. KOH gives mainly
Text Solution
|
- Grignard reagent is obtained when magnesium is treated with
Text Solution
|
- Ethylene reacts bromine to form-
Text Solution
|
- C(2)H(4) overset(Br(2))rarr X overset(KCN)rarr Y, Y is
Text Solution
|
- Reactivity order of halides for dehydrohalogenation is : -
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substiution...
Text Solution
|
- The correct reactivity order of alcohols towards H-X will be (I) CH(...
Text Solution
|
- Identify 'Z' in the following reaction series, CH(3)CH(2)CH(2)Brover...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction C(2)H(5) OH + HX to C2 H(5) X + H(2)O , the order of ...
Text Solution
|
- Ethyl alcohol reacts at a faster rate with HI than with HCl in forming...
Text Solution
|