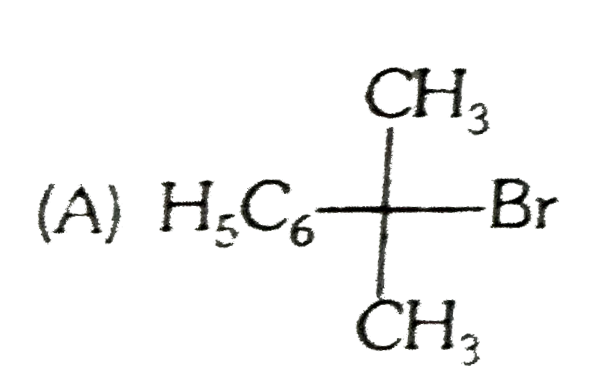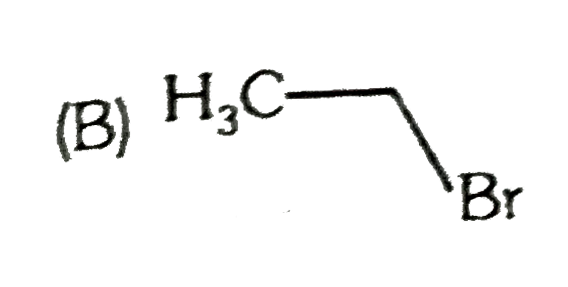A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALLEN-ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDE-EXERCISE
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions generally expressed as Nu^(-) +R...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions generally expressed as Nu^(-) +R...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution reaction is mainly of two types: S...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution reaction is mainly of two types: S...
Text Solution
|
- Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution reaction is mainly of two types: S...
Text Solution
|
- An optically active compound A (assume dextrorotatory) has the molecul...
Text Solution
|
- An optically active compound A (assume dextrorotatory) has the molecul...
Text Solution
|
- Select the member of each pair that shows rate of S(N)2 reaction with ...
Text Solution
|
- Of the following statements which are true for S(N)1 reaction. (a) T...
Text Solution
|
- Of the following statements , which are true for S(N)2 reaction. (a)...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the isomers of molecular formula C(4)H(9)CI in order of decrea...
Text Solution
|
- There is an overall 29-fold difference in reactivity of 1-chlorohexane...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the product when A reacts with
Text Solution
|
- Which is faster in the following pairs of halogen compounds undergoing...
Text Solution
|
- R -Mg-Br(A) on reaction with H(2)O forms a gas (B), which occupied 1.4...
Text Solution
|
- Provide structure of major product in the following reaction indicatin...
Text Solution
|
- Propose mechanism of the following reactions:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following alkyl halide could be successfully used to synt...
Text Solution
|
- An alkyl bromide A has molecular formula C(8)H(17)Br and four differen...
Text Solution
|
- Identify A to G in the following. (a) overset(Br(2), C Cl(4))rarr A...
Text Solution
|