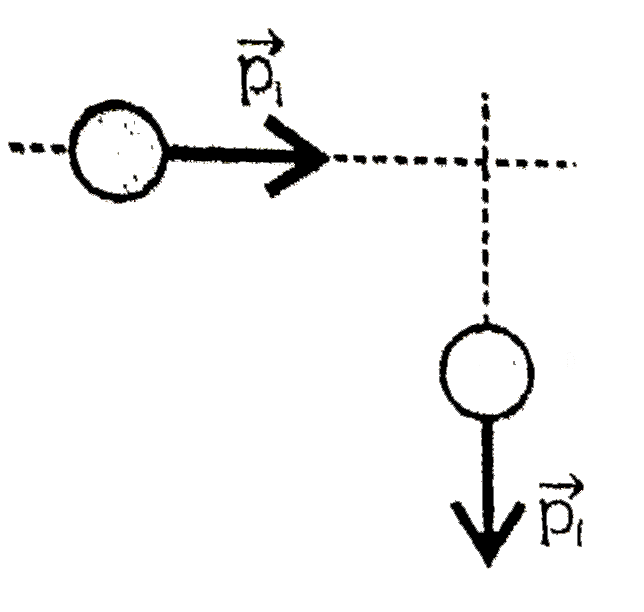A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-II|43 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-III|42 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-V B|19 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-IV ASSERTION & REASON|11 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise 5 B (Integer Type Questions)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-CENTRE OF MASS-EXERCISE-I
- Two blocks A(3 kg) and B(2 kg) resting on a smooth horizontal surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A shell is fired vertically upwards with a velocity v(1) from the deck...
Text Solution
|
- A shell is fired from a cannon with a velocity V at an angle theta wit...
Text Solution
|
- A ball hits a floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision. In this...
Text Solution
|
- Three balls A, B and C are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Give...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 1 kg strikes elastically with another body at rest and ...
Text Solution
|
- A small bucket of mass M is attached to a long inextensible cord of le...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, a particle P strikes the inclined smooth plane ho...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 2m impinges directly on a ball of mass m, which is at r...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2 kg is projected upward from the surface of the ground...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 1 kg strikes a heavy plarform elastically, moving upwar...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of mass m, constrained to move along the circumference o...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles start moving from the same point along the same straight...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rope of linear mass density lambda and length l is coiled on...
Text Solution
|
- A 10 g rubber ball and a 10g clay ball are each thrown at a wall with ...
Text Solution
|
- Two friends are sitting in a stationary boat. At t = 30s the person at...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2)(m(1) gt m(2)) connected by a massle...
Text Solution
|
- A small puck is sliding to the right with momentum vec(P)(1) on a hori...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth sphere is moving on a horizontal surface with velocity vector...
Text Solution
|
- A moving 2 kg ball with a speed of 2 ms^(-1) hits obliquely a stationa...
Text Solution
|