Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-V A|20 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-V B|19 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-IV A|32 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS &VECTORS
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-IV ASSERTION & REASON|11 VideosELASTICITY, SURFACE TENSION AND FLUID MECHANICS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise 5 B (Integer Type Questions)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-CENTRE OF MASS-EXERCISE-IV B
- A bullet ofmass m is fired with a velocity 10m//s at angle theta with...
Text Solution
|
- An object of mass 5 kg is projected with a velocity of 20 m s^(-1) at ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected by a massless pulley ...
Text Solution
|
- The 4 kg sphere form rest when theta = 60^(@) strikes a block mass of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of mass m each are attached to a light rod of length d, ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles, each of mass m, are connected by a light inextensible s...
Text Solution
|
- After perfectly inelastic collision between two identical balls moving...
Text Solution
|
- In transistor, the change in base current from 400 microampere to 425 ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles each of mass m are connected by a light inextensible str...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 1kg is attached to an inextensible string. The ball is ...
Text Solution
|
- A wedge of mass M = 2m rests on a smooth horizontal plane. A small blo...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass in m= 1 kg is hung vertically by a thread of length l =...
Text Solution
|
- A 70 g ball B dropped from a height h(0) = 9m reaches a height h(2) = ...
Text Solution
|
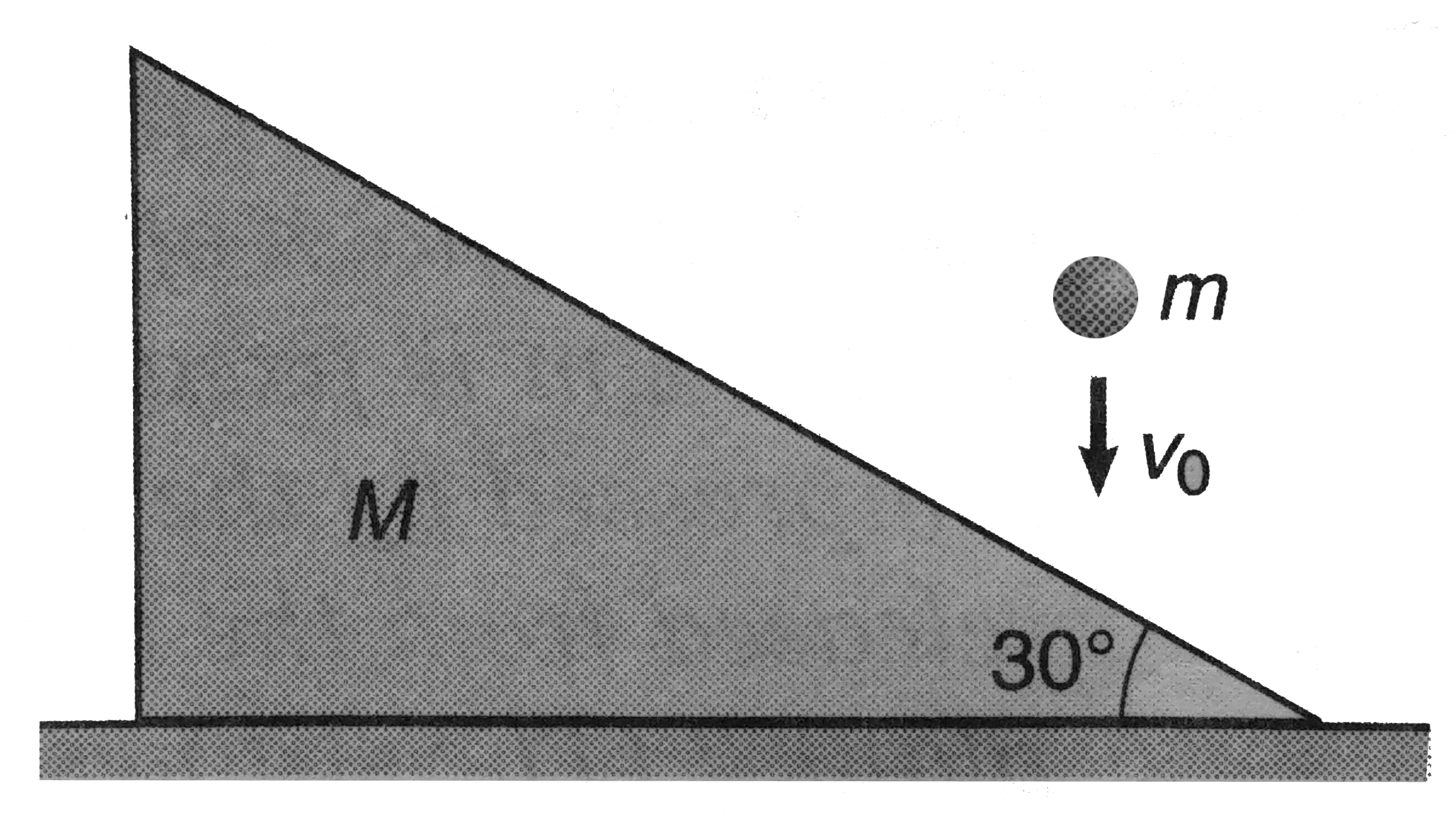
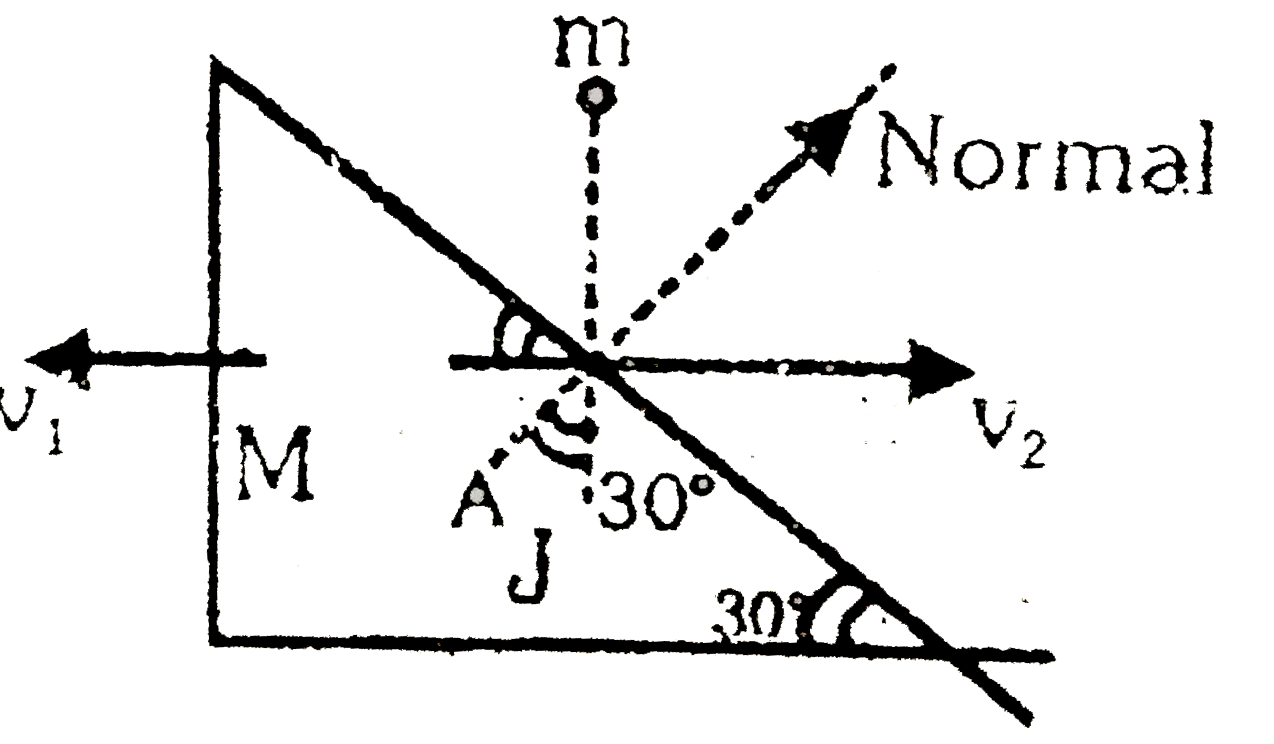
- A ball of mass m=1kg falling vertically with a velocity v0=2m//s strik...
Text Solution
|