A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
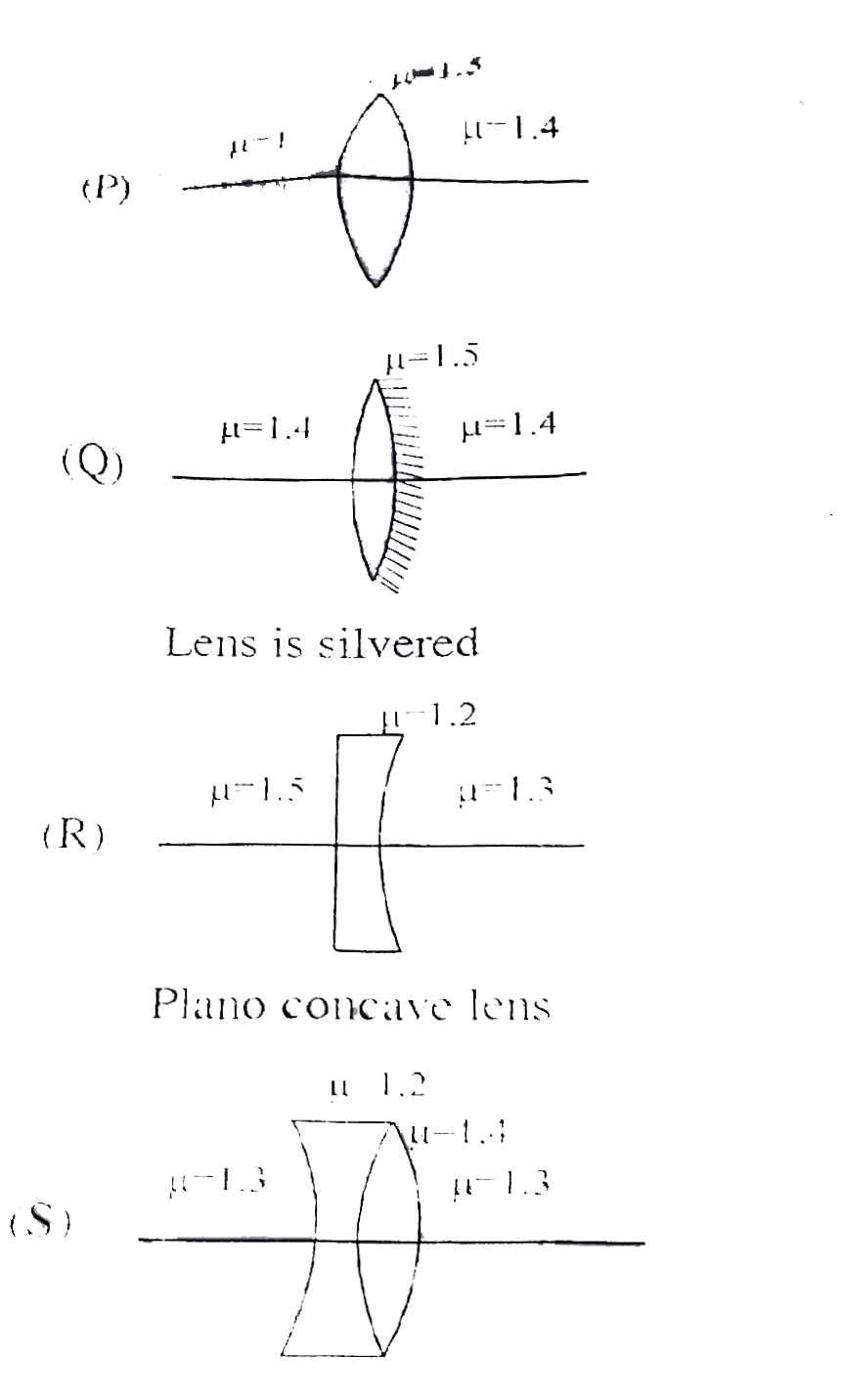
- List-I gives different lens configurations. The radius of curvature of...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an equiconvex lens of radius of curvature R and focal length ...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light coming from infinty is passing through a biconvex lens...
Text Solution
|
- A double convex thin lens made of glass (refractive index mu = 1.5) h...
Text Solution
|
- A lens of refractive index mu becomes a lens of focal length f' when i...
Text Solution
|
- एक द्वि-उत्तल लेन्स के दोनों पृष्ठों की वक्रता त्रिज्या R है। लेन्स के...
Text Solution
|
- काँच (अपवर्तनांक,mu=1.5 ) के एक उभयोत्तल पतले लेन्स की प्रत्येक वक्...
Text Solution
|
- यदि किसी उत्तल लेंस पर आपतित किरण लेंस के अक्ष के समांतर है, तो वह लें...
Text Solution
|
- एक समोत्तल लेंस के पदार्थ का अपवर्तनांक 1.5 है। लेंस की फोकस दूरी f तथ...
Text Solution
|