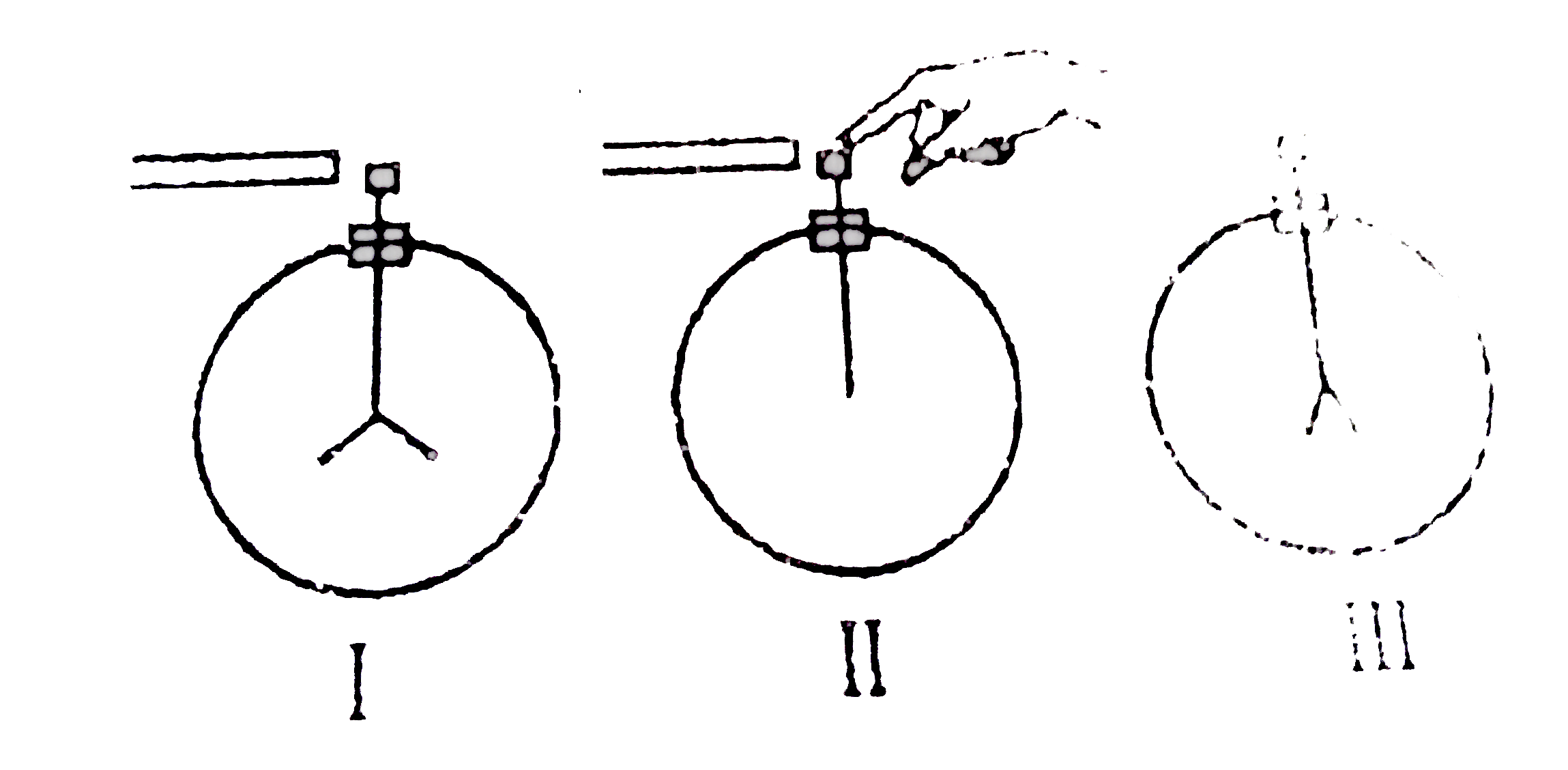A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise Exersice-03|7 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise ASSERTION-REASON|18 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise Part -II Example Some worked out Examples|1 VideosKINEMATICS (MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE AND MOTION IN A PLANE)
ALLEN|Exercise BEGINNER S BOX-7|8 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD, UNITS AND DIMENSIONS & ERRORS IN MEASUREMENT
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-IV|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-MISCELLANEOUS-Exercise-01
- The method of dimensional analysis can be used to derive which of the ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle with mass m and initial speed V(0) is a subject to a veloci...
Text Solution
|
- When a negative charged rod is brought near, but does not touch, the i...
Text Solution
|
- Two small insulating spheres are attached to silk threads. The spheres...
Text Solution
|
- Using mass(M),length(L),time(T) and current (A) as fundamental quantit...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges +9e and +e are kept 16 cm. Apart from each other. Wh...
Text Solution
|
- Four charges are arranged at the corners of a square ABCD, as shown in...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal positive charges Q are fixed at points (a, 0) and (-a,0) on ...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal negative charges -q each are fixed at points (0,-a) and (0,a...
Text Solution
|
- Figure below show regular hexagons, with charges at the vertices. In w...
Text Solution
|
- Two infinite linear charges are placed parallel to each other at a dis...
Text Solution
|
- An electron of mass M(e), initially at rest, moves through a certain d...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is projected as in figure with kinetic energy K, at an ang...
Text Solution
|
- A proton sists at coordinates (x,y)=(0, 0), and an electron at (d, h),...
Text Solution
|
- A positive point charge 50mu C is located in the plane xy at a point w...
Text Solution
|
- Three point charges of 1C, 2C and 3C are placed at the corners of an e...
Text Solution
|
- Rank the work required to assemble the charge distribution below from ...
Text Solution
|
- The are AB with the centre C and infinitely long wire having linear ch...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram shows the electric field lines produced by an electrostali...
Text Solution
|
- A charge +q is placed at the origin O of x-y axes as shoen in the figu...
Text Solution
|