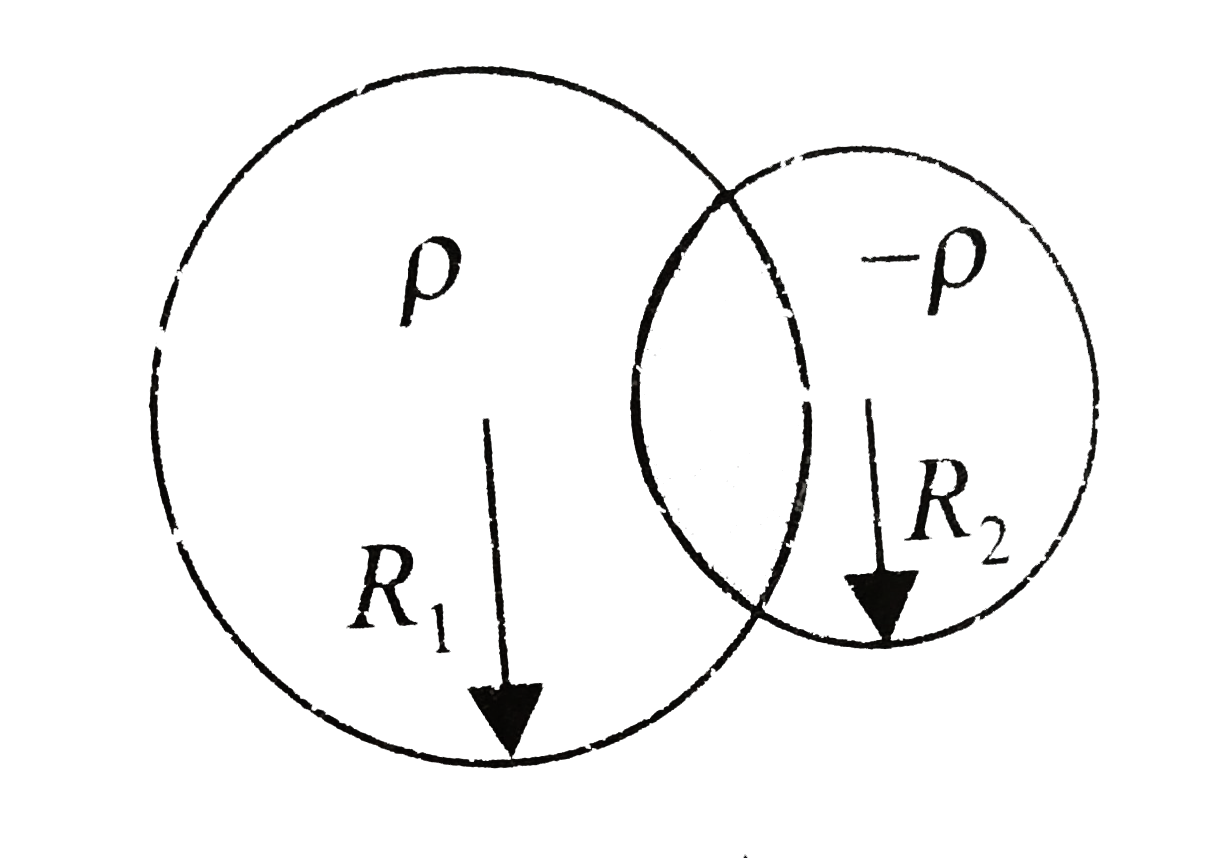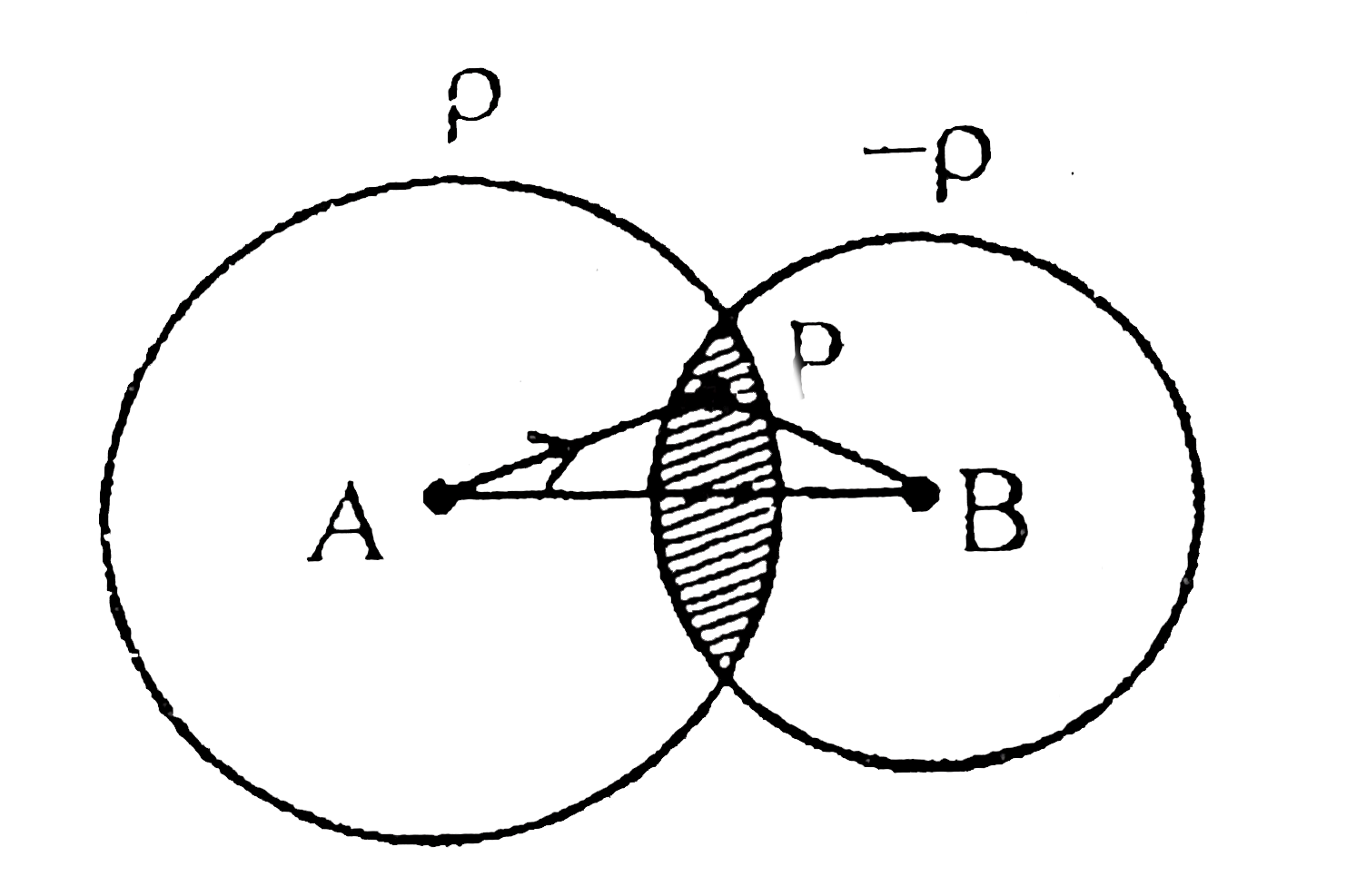A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise REASONING TYPE|1 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise MATCH THE COLUME TYPE|1 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN|Exercise Exercise-05(B)|19 VideosKINEMATICS (MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE AND MOTION IN A PLANE)
ALLEN|Exercise BEGINNER S BOX-7|8 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD, UNITS AND DIMENSIONS & ERRORS IN MEASUREMENT
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-IV|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-MISCELLANEOUS-MCQ s WITH ONE OR MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER
- A positively charged thin metla ring of radius R is fixed in the X-Y p...
Text Solution
|
- A nonconducting solid sphere of radius R is uniformly charged. The mag...
Text Solution
|
- An elliptical cavity is carved with in a prefect conductor figure. A ...
Text Solution
|
- For spherical symmetrical charge distribution, variation of electric p...
Text Solution
|
- Two nonconducting solid spheres of radii R and 2R, having uniform volu...
Text Solution
|
- Two nonconducting spheres of radii R1 and R2 and carrying uniform volu...
Text Solution
|