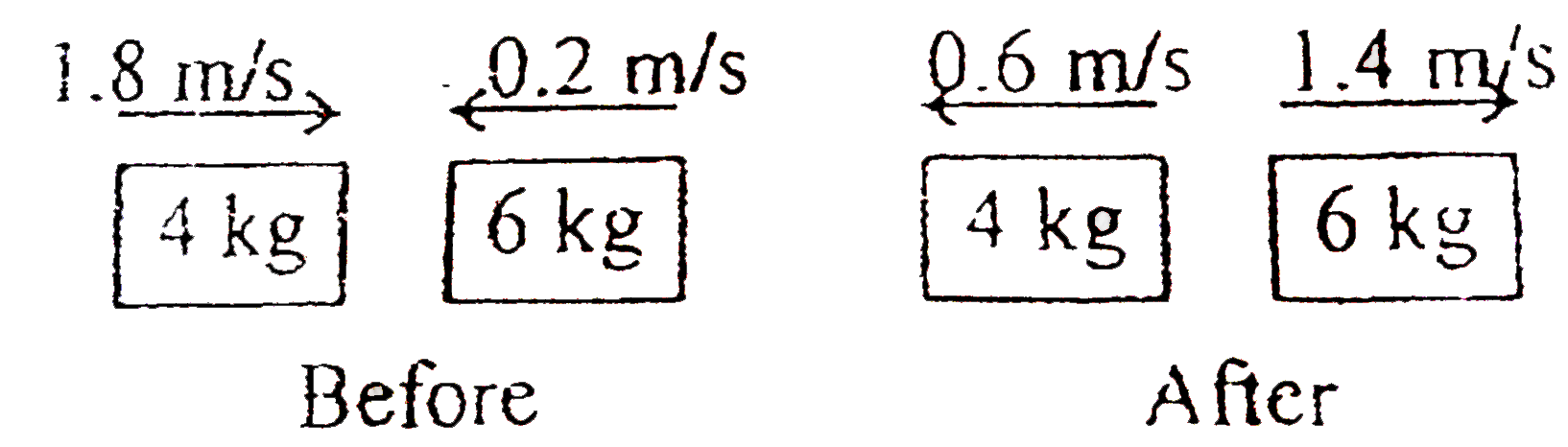A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-TEST PAPER-Exercise (Physics)
- A 6.0kg mass is moving to the right at 10 m//s. A 0.25kg mass is fired...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical balls moving in opposite directions in free space collid...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, determine the character of the collision. The masses of the...
Text Solution
|
- A rod has non uniform mass distribution. The mass increases uniformly ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid hemisphere and a hemisphereical shell are joined as shown. Bot...
Text Solution
|
- In a system of four thin uniform rods are each of mass inas shown. If ...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical rectangular door with its centre of gravity at O (see figur...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular metal plate ABCD is supported by two hinges P(1) and P(2...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform beam of weight W is attached to a verical wall by a hings H....
Text Solution
|
- A body is free to rotate about an axis parallel to y-axis. A force of ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R=2m starts rotating wth constant angular acceleratio...
Text Solution
|
- In the balance machine shown in the figures. Which arm will move downw...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M =2.50 kg and radius R = 0.20 m is mounted on ...
Text Solution
|
- A car runs at constant speed around the horizontal race track shown in...
Text Solution
|
- A man M slides down a curved frictionless track, starting from rest. ...
Text Solution
|
- An object moves counter-clockwise along the circular path shown below....
Text Solution
|
- A girl finds herself stuck with her back to the wall of a cylinder rot...
Text Solution
|
- A puck of mass m is moving in a circle at constant speed on a friction...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of bob of mass m and length L has one of its ends fi...
Text Solution
|
- A small disc can slide in a circular path on a frictionless inclined p...
Text Solution
|