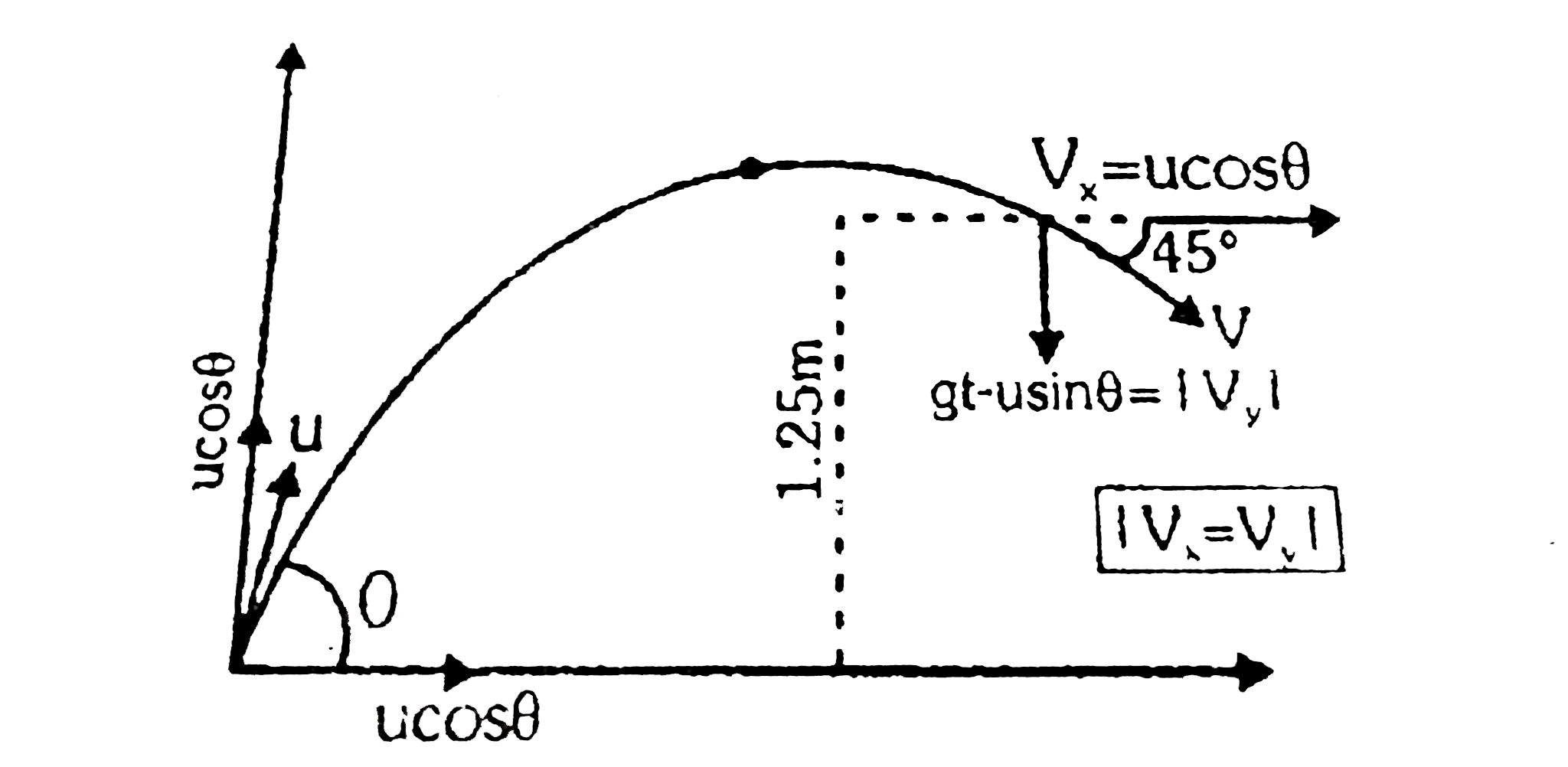Let 't' be the time after which the stone hits the object and `theta` be the abgle which the velocity vector `vec(u)` makes with horizontal. According to question, we have following three conditions.
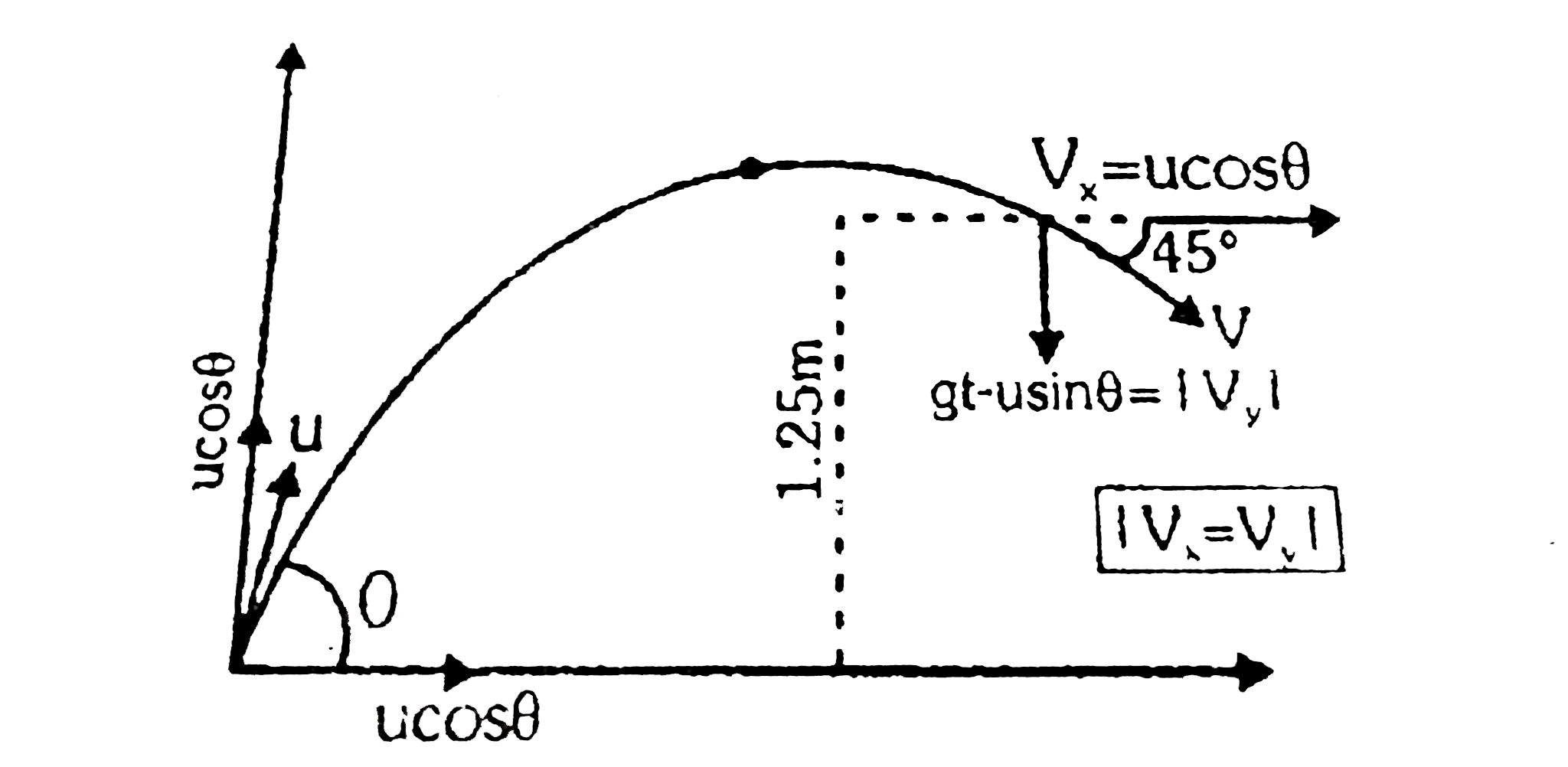
(i) Vertical displacement of stome is `1.25 m`
`:' 1.25=(u sin theta)t-1/2 g t^(2)` where `g=10 m//s^(2)`
`rArr (u sin theta)t=1.25+5t^(2)` ...(i)
(ii) horizontal displacement of stone
`=3 +` dispplacement of object A.
Therefore `(u cos theta)t=3 +1/2 at^(2)`
where `a=1.5 m//s^(2) rArr (u cos theta)t=3 +0.75 t^(2)` ...(ii)
Horizontal component of velocity (of stone)
`=` vertical component (because velocity vector is inclined) at `45^(@)` with horizontal.
Therefore `(u cos theta)=g t-(u sin theta)` ...(iii)
The right hand side is written `g t-u sin theta` because the stone is in its downward motion.
Therefore, `g t gt u sin theta`
In upward motion `u sin theta gt g t`
Multiplying equation (iii) with t we can write,
`(u cos theta) t+(u sin theta)t=10 t^(2)` ...(iv)
Now `(iv)-(ii)-(i)` gives `4.25 t^(2)-4.25=0` or `t=1 s`
Substituting `t=1s` in (i) and (ii) we get
`u sin theta=6.25 m//s`
`rArr u_(y)=6.25 m//s` and `u cos theta=3.75 m//s`
`rArr u_(x)=3.75 m//s` therefore `vec(u)=u_(x)hat(i)+u_(y)hat(j)`
`rArr vec(u)=(3.75hat(i)+6.25hat(j)) m//s`